Android Studio JNI开发基础篇
- 前言
- 环境搭建
- 创建Native代码
- 使用
前言
开发进程中,为了数据交互安全,决定对数据进行des加密,然落后行前后交互;但是,如果密钥放置在android代码里面,就算是混淆,反编译也很容易让人拿到密钥,数据加密的安全度不高,因此斟酌通过jni来返回1个密钥对数据进行加解密。从而到达数据的安全性。
环境搭建
下载NDK
通过android studio去下载NDK插件;打开File–>Project Structure–>SDK Location–>Android NDK Location,以下图:
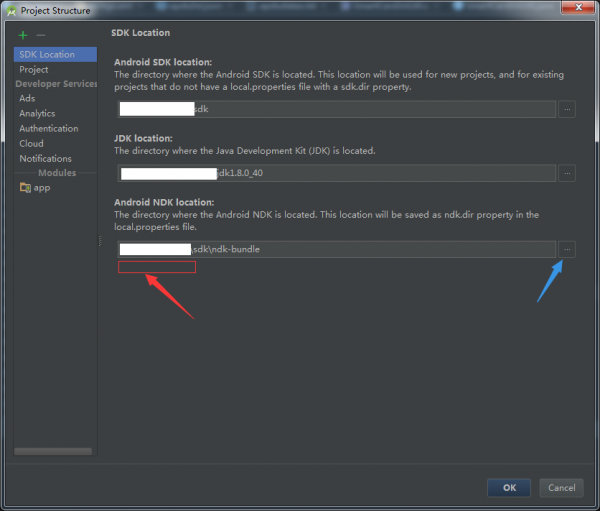
如果是第1次,没有下载NDK插件,在红色箭头的地方有个按钮用于下载安装,点击等待下载便可,使用AS下载的NDK会默许反正你的sdk的目录路径下;亦或选中蓝色剪头的按钮选择已下载好的NDK;点击“OK”,配置成功以后,会在local.properties文件下看见相应的路径指向,以下图:
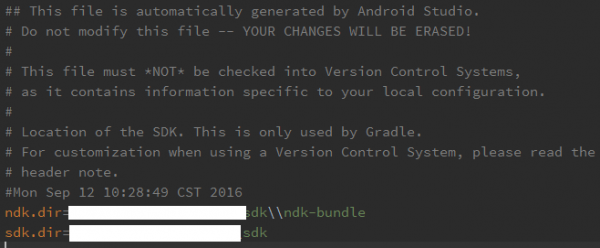
配置NDK环境变量
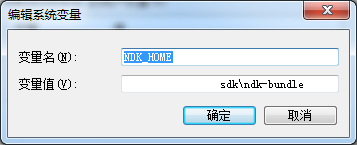
创建NDK_HOME
右键我的电脑–>属性–>高级系统设置–>环境变量–>系统变量–>新建–>创建1个“NDK_HOME”,NDK的路径就是上1步中配置的路径,以下图:
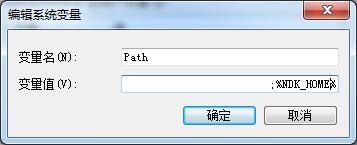
添加path
在系统变量中找到Path–>编辑,将;%NDK_HOME%添加至path中,以下图:
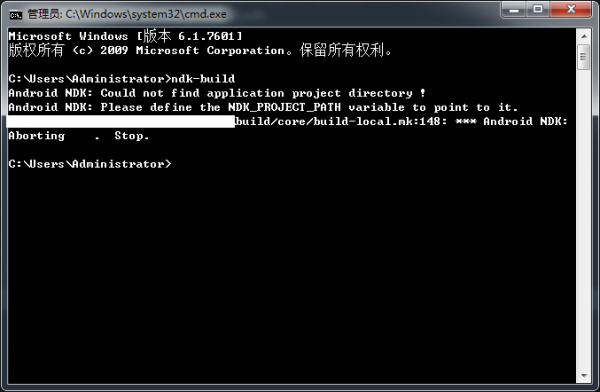
验证配置是不是成功
在cmd下输入“ndk-build”指令,如果出现下图结果,即配置成功:
创建Native代码
在java目录下创建1个带有native方法的java文件
/** * native */ public class SmartCardJniUtil { /** * 加载so库 */ static { System.loadLibrary("SCJniUtil"); } /** * 获得密钥 * @return 密钥 */ public native String getKey(); }通过Build–>Make Project项目
成功以后,在app–>intermediates–>classes–>debug–>个人项目路径下找到上面新建的native类的class文件,以下图:


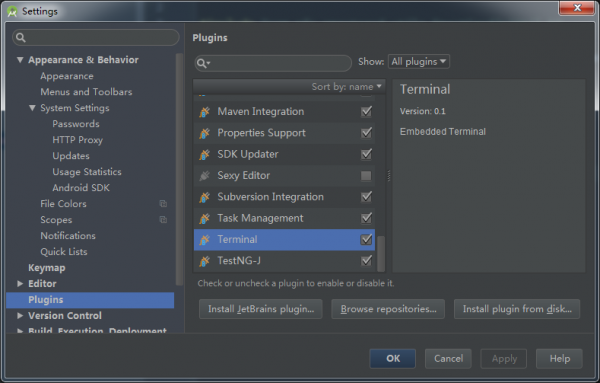
生成头文件
在File—settings—plugins下勾选Termainal
指令生成头文件
javah -d jni -classpath ;….\build\intermediates\classes\debug 类的包名。
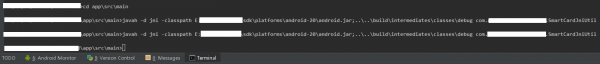
按着以上说明,首先通过cd app\src\main跳转到main目录下,然后输入以下指令:
javah -d jni -classpath E:**\sdk\platforms\android⑵0\android.jar;….\build\intermediates\classes\debug com.a.b.c.SmartCardJniUtil
以下图:
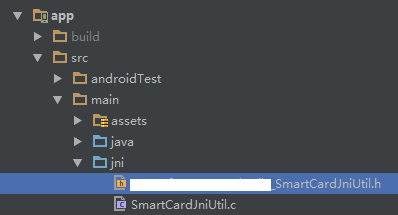
成功以后会在main目录下多1个jni文件,并包括了1个.h的头文件,以下图:
创建.c文件
在jni目录下右键–>New–>C/C++ Source File创建1个SmartCardJniUtil.c文件,然后引入头文件,返回密钥,以下代码:#include "com_a_b_c_SmartCardJniUtil.h" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_a_b_c_SmartCardJniUtil_getKey (JNIEnv *env, jobject jobject1) { return (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, "1122334455667788"); };
在build.gradle文件下添加配置,代码以下:
buildTypes { release { minifyEnabled true proguardFiles getDefaultProguardFile('proguard-android.txt'), 'proguard-rules.pro' ndk { moduleName "SCJniUtil" //生成的so名字 abiFilters "armeabi", "armeabi-v7a", "x86" //输出指定3种abi体系结构下的so库。 } } debug { ndk { moduleName "SCJniUtil" //生成的so名字 abiFilters "armeabi", "armeabi-v7a", "x86" //输出指定3种abi体系结构下的so库。 } } } sourceSets { main { jniLibs.srcDirs = ['libs'] } }清算并重新make项目,生成so库,以下图:
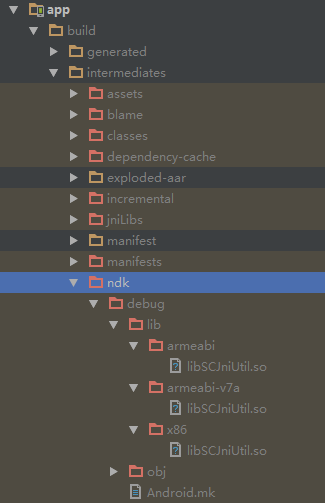
关于Android.mk文件说明
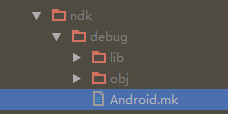
通过eclipse开发jni的时候,需要进行1个Android.mk文件的配置,但是Android Studio中并没有做,没有做不代表没有,AS自动帮我们生成了,不需要我们自己去创建并配置,以下图:
混淆文件中添加不混淆native的配置
-keepclasseswithmembernames class * { native <methods>; }
使用
通过jni获得密钥
当以上步骤完成以后,实例化native对象,调用相应的方法便可获得到相应的结果,代码以下://实例化对象 SmartCardJniUtil jniUtil = new SmartCardJniUtil(); //获得密钥 jniUtil.getKey()des加解密工具
public class DesUtil { /** * 数据加密,算法(DES) * * @param data 要进行加密的数据 * @return 加密后的数据 */ public static String encryptBasedDes(String data, String keyStr) { keyStr = StringUtilsSimple.leftPad(keyStr, 16, "0"); byte[] DES_KEY = ByteUtil.hexStr2Byte(keyStr); String encryptedData = null; try { // DES算法要求有1个可信任的随机数源 SecureRandom sr = new SecureRandom(); DESKeySpec deskey = new DESKeySpec(DES_KEY); // 创建1个密匙工厂,然后用它把DESKeySpec转换成1个SecretKey对象 SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES"); SecretKey key = keyFactory.generateSecret(deskey); // 加密对象 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES"); cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, sr); // 加密,并把字节数组编码成字符串 encryptedData = ByteUtil.hexToStr(cipher.doFinal(data.getBytes())); } catch (Exception e) { // log.error("加密毛病,毛病信息:", e); throw new RuntimeException("加密毛病,毛病信息:", e); } return encryptedData; } /** * 数据解密,算法(DES) * * @param cryptData 加密数据 * @return 解密后的数据 */ public static String decryptBasedDes(String cryptData, String keyStr) { keyStr = StringUtilsSimple.leftPad(keyStr, 16, "0"); byte[] DES_KEY = ByteUtil.hexStr2Byte(keyStr); String decryptedData = null; try { // DES算法要求有1个可信任的随机数源 SecureRandom sr = new SecureRandom(); DESKeySpec deskey = new DESKeySpec(DES_KEY); // 创建1个密匙工厂,然后用它把DESKeySpec转换成1个SecretKey对象 SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES"); SecretKey key = keyFactory.generateSecret(deskey); // 解密对象 Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES"); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, sr); // 把字符串解码为字节数组,并解密 decryptedData = new String(cipher.doFinal(ByteUtil.hexStr2Byte(cryptData))); } catch (Exception e) { // log.error("解密毛病,毛病信息:", e); throw new RuntimeException("解密毛病,毛病信息:", e); } return decryptedData; } public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String str = "123456789"; // DES数据加密 long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); String s1 = encryptBasedDes(str, "1122334411223344"); System.out.println("time1:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time)); System.out.println(s1); // DES数据解密 long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); String s2 = decryptBasedDes(s1, "1122334411223344"); System.out.println("time2:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - time2)); System.err.println(s2); } }文本左右补位的工具
public class StringUtilsSimple { /** * A String for a space character. * * @since 3.2 */ public static final String SPACE = " "; /** * <p>The maximum size to which the padding constant(s) can expand.</p> */ private static final int PAD_LIMIT = 8192; // Empty checks // ----------------------------------------------------------------------- /** * <p> * Checks if a CharSequence is empty ("") or null. * </p> * * <pre> * StringUtils.isEmpty(null) = true * StringUtils.isEmpty("") = true * StringUtils.isEmpty(" ") = false * StringUtils.isEmpty("bob") = false * StringUtils.isEmpty(" bob ") = false * </pre> * * <p> * NOTE: This method changed in Lang version 2.0. It no longer trims the * CharSequence. That functionality is available in isBlank(). * </p> * * @param cs * the CharSequence to check, may be null * @return {@code true} if the CharSequence is empty or null * @since 3.0 Changed signature from isEmpty(String) to * isEmpty(CharSequence) */ public static boolean isEmpty(final CharSequence cs) { return cs == null || cs.length() == 0; } /** * <p> * Left pad a String with a specified String. * </p> * * <p> * Pad to a size of {@code size}. * </p> * * <pre> * StringUtils.leftPad(null, *, *) = null * StringUtils.leftPad("", 3, "z") = "zzz" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 3, "yz") = "bat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 5, "yz") = "yzbat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 8, "yz") = "yzyzybat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 1, "yz") = "bat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", -1, "yz") = "bat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 5, null) = " bat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 5, "") = " bat" * </pre> * * @param str * the String to pad out, may be null * @param size * the size to pad to * @param padStr * the String to pad with, null or empty treated as single space * @return left padded String or original String if no padding is necessary, * {@code null} if null String input */ public static String leftPad(final String str, final int size, String padStr) { if (str == null) { return null; } if (isEmpty(padStr)) { padStr = SPACE; } final int padLen = padStr.length(); final int strLen = str.length(); final int pads = size - strLen; if (pads <= 0) { return str; // returns original String when possible } if (padLen == 1 && pads <= PAD_LIMIT) { return leftPad(str, size, padStr.charAt(0)); } if (pads == padLen) { return padStr.concat(str); } else if (pads < padLen) { return padStr.substring(0, pads).concat(str); } else { final char[] padding = new char[pads]; final char[] padChars = padStr.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < pads; i++) { padding[i] = padChars[i % padLen]; } return new String(padding).concat(str); } } /** * <p>Left pad a String with a specified character.</p> * * <p>Pad to a size of {@code size}.</p> * * <pre> * StringUtils.leftPad(null, *, *) = null * StringUtils.leftPad("", 3, 'z') = "zzz" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 3, 'z') = "bat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 5, 'z') = "zzbat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", 1, 'z') = "bat" * StringUtils.leftPad("bat", -1, 'z') = "bat" * </pre> * * @param str the String to pad out, may be null * @param size the size to pad to * @param padChar the character to pad with * @return left padded String or original String if no padding is necessary, * {@code null} if null String input * @since 2.0 */ public static String leftPad(final String str, final int size, final char padChar) { if (str == null) { return null; } final int pads = size - str.length(); if (pads <= 0) { return str; // returns original String when possible } if (pads > PAD_LIMIT) { return leftPad(str, size, String.valueOf(padChar)); } return repeat(padChar, pads).concat(str); } /** * <p>Returns padding using the specified delimiter repeated * to a given length.</p> * * <pre> * StringUtils.repeat('e', 0) = "" * StringUtils.repeat('e', 3) = "eee" * StringUtils.repeat('e', -2) = "" * </pre> * * <p>Note: this method doesn't not support padding with * <a href="http://www.unicode.org/glossary/#supplementary_character">Unicode Supplementary Characters</a> * as they require a pair of {@code char}s to be represented. * If you are needing to support full I18N of your applications * consider using {@link #repeat(String, int)} instead. * </p> * * @param ch character to repeat * @param repeat number of times to repeat char, negative treated as zero * @return String with repeated character * @see #repeat(String, int) */ public static String repeat(final char ch, final int repeat) { final char[] buf = new char[repeat]; for (int i = repeat - 1; i >= 0; i--) { buf[i] = ch; } return new String(buf); } /** * <p>Right pad a String with a specified String.</p> * * <p>The String is padded to the size of {@code size}.</p> * * <pre> * StringUtils.rightPad(null, *, *) = null * StringUtils.rightPad("", 3, "z") = "zzz" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 3, "yz") = "bat" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 5, "yz") = "batyz" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 8, "yz") = "batyzyzy" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 1, "yz") = "bat" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", -1, "yz") = "bat" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 5, null) = "bat " * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 5, "") = "bat " * </pre> * * @param str the String to pad out, may be null * @param size the size to pad to * @param padStr the String to pad with, null or empty treated as single space * @return right padded String or original String if no padding is necessary, * {@code null} if null String input */ public static String rightPad(final String str, final int size, String padStr) { if (str == null) { return null; } if (isEmpty(padStr)) { padStr = SPACE; } final int padLen = padStr.length(); final int strLen = str.length(); final int pads = size - strLen; if (pads <= 0) { return str; // returns original String when possible } if (padLen == 1 && pads <= PAD_LIMIT) { return rightPad(str, size, padStr.charAt(0)); } if (pads == padLen) { return str.concat(padStr); } else if (pads < padLen) { return str.concat(padStr.substring(0, pads)); } else { final char[] padding = new char[pads]; final char[] padChars = padStr.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0; i < pads; i++) { padding[i] = padChars[i % padLen]; } return str.concat(new String(padding)); } } /** * <p>Right pad a String with a specified character.</p> * * <p>The String is padded to the size of {@code size}.</p> * * <pre> * StringUtils.rightPad(null, *, *) = null * StringUtils.rightPad("", 3, 'z') = "zzz" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 3, 'z') = "bat" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 5, 'z') = "batzz" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", 1, 'z') = "bat" * StringUtils.rightPad("bat", -1, 'z') = "bat" * </pre> * * @param str the String to pad out, may be null * @param size the size to pad to * @param padChar the character to pad with * @return right padded String or original String if no padding is necessary, * {@code null} if null String input * @since 2.0 */ public static String rightPad(final String str, final int size, final char padChar) { if (str == null) { return null; } final int pads = size - str.length(); if (pads <= 0) { return str; // returns original String when possible } if (pads > PAD_LIMIT) { return rightPad(str, size, String.valueOf(padChar)); } return str.concat(repeat(padChar, pads)); } }
上一篇 浅谈Android os体系架构