React Native之底层源码分析篇
学习React-Native有1段时间了。今天就从源码的角度来分析下React-Native底层的通讯机制。了解下底层是如何通讯的对开发也有所好处。
概要
先大概讲1下React-Native的通讯进程。RN主要的通讯在于java与js之间,平常我们写的jsx代码终究会调用到原生的View。上1篇博客我们也了解到了要新建1个原生模块需要在java层和js层分别写1个Module,那这彼此之间联系是如何实现的呢?
层次结构
RN总共分为3层,java层,C++层,js层。借用1幅图来看下:
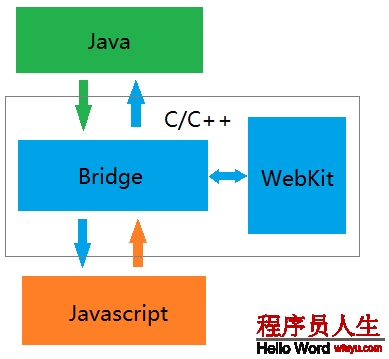
Java层:java层就是app原生代码,它通过启动C++层的javascript解析器javascriptCore来履行js代码,从而构建原生UI等。java层依赖于众多优秀开源库,在图片处理使用的是Fresco,网络通讯使用的是okhttp,Json解析工具用jackson,动画库用NineOldAndroids等,在java层原生的功能均封装为Module,如Toast和Log等。
C++层:c++层最主要是封装了JavaScriptCore,它是1个全新的支持ES6的webKit。Bridge连接了java与js之间的通讯。解析js文件是通过JSCExectutor进行的。
Js层:主要处理事件分发及UI Layout,平常开发最经常使用的。通用jsx来写业务代码,通过flexbox来实现布局。不依赖DOM。由于react有 DOM diff这个算法,所以它的效力非常高。
通讯机制
在Java层与Js层的bridge分别存有相同1份模块配置表,Java与Js相互通讯时,通过将里配置表中的moduleID,methodID转换成json数据的情势传递给到C++层,C++层传送到js层,通过js层的的模块配置表找到对应的方法进行履行,如果有callback,则回传给java层。这里只是大概介绍,后面会有详细讲授。
主要流程与主要类
先看下java层的流程图:
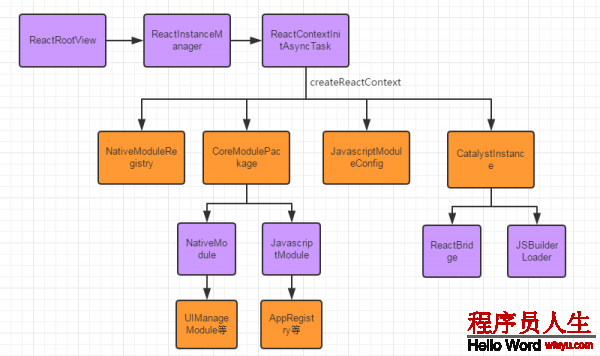
- ReactInstanceManager:主要是用来创建及管理CatalyInstance的实例的上层接口,控制开发调试,生命周期与ReactRootView所在activity保持1致。
- ReactRootView:为启动入口核心类,负责监听及分发事件并重新渲染元素,App启动后,其将作为App的root view。
- CatalystInstance:提供Java与Js互通的环境,创建Java模块注册表及Javascript模块注册表,并遍历实例化模块,最后通过ReactBridge将Js Bundle传送到Js引擎。
- JSBuilderLoader:缓存了JsBundle的信息,封装了上层加载JsBundle相干接口,CatalystInstance通过其间接调用ReactBridge去加载文件。
- NativeModuleRegistry:Java层模块注册表,即暴露给Js的API集合。
- JavascriptModuleRegistry:Js层模块注册表,负责将所有JavaScriptModule注册到CatalystInstance。
- CoreModulePackage:CoreModulesPackage里面定义了RN框架核心的1些Java和JS的module,创建NativeModules&JsModules组件模块。
源码分析
加载Module
首先看MainActivity的
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
return Arrays.<ReactPackage>asList(
new MainReactPackage(),
new AppReactPackage()
);
}AppReactPackage是我们自定义的1个ReactPackage,也就是说如果自己定义了新组件,要在这里添加。看下ReactActivity,看它的onCreate方法:
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
if(this.getUseDeveloperSupport() && VERSION.SDK_INT >= 23 && !Settings.canDrawOverlays(this)) {
Intent mReactRootView = new Intent("android.settings.action.MANAGE_OVERLAY_PERMISSION");
this.startActivity(mReactRootView);
FLog.w("React", "Overlay permissions needs to be granted in order for react native apps to run in dev mode");
Toast.makeText(this, "Overlay permissions needs to be granted in order for react native apps to run in dev mode", 1).show();
}
this.mReactInstanceManager = this.createReactInstanceManager();
ReactRootView mReactRootView1 = this.createRootView();
mReactRootView1.startReactApplication(this.mReactInstanceManager, this.getMainComponentName(), this.getLaunchOptions());
this.setContentView(mReactRootView1);
}
主要完成3个功能,通过createReactInstanceManager创建ReactInstanceManager,它主要是用来创建及管理CatalyInstance的实例的上层接口。第2步是通过createRootView来创建ReactRootView。最后调用ReactRootView的startReactApplication来启动利用,并把它当作rootview setContentView到界面上。重点看startReactApplication方法:
public void startReactApplication(ReactInstanceManager reactInstanceManager, String moduleName, @Nullable Bundle launchOptions) {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
Assertions.assertCondition(this.mReactInstanceManager == null, "This root view has already been attached to a catalyst instance manager");
this.mReactInstanceManager = reactInstanceManager;
this.mJSModuleName = moduleName;
this.mLaunchOptions = launchOptions;
if(!this.mReactInstanceManager.hasStartedCreatingInitialContext()) {
this.mReactInstanceManager.createReactContextInBackground();
}
if(this.mWasMeasured && this.mIsAttachedToWindow) {
this.mReactInstanceManager.attachMeasuredRootView(this);
this.mIsAttachedToInstance = true;
this.getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(this.getKeyboardListener());
} else {
this.mAttachScheduled = true;
}
}mJSModuleName是与前端约定好所要启动的JS Application Name。先看createReactContextInBackground方法,它位于ReactInstanceManager的实现类ReactInstanceManagerImpl中:
public void recreateReactContextInBackground() {
Assertions.assertCondition(this .mHasStartedCreatingInitialContext , "recreateReactContextInBackground should only be called after the initial createReactContextInBackground call.") ;
this. recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner() ;
}createReactContextInBackground终究调用到recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner:
private void recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner() {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
if( this.mUseDeveloperSupport && this.mJSMainModuleName != null) {
if (this.mDevSupportManager.hasUpToDateJSBundleInCache()) {
this .onJSBundleLoadedFromServer() ;
} else if(this .mJSBundleFile == null) {
this .mDevSupportManager.handleReloadJS() ;
} else {
this .mDevSupportManager.isPackagerRunning( new PackagerStatusCallback() {
public void onPackagerStatusFetched( final boolean packagerIsRunning) {
UiThreadUtil.runOnUiThread( new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if(packagerIsRunning) {
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this .mDevSupportManager.handleReloadJS() ;
} else {
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this .recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleFile() ;
}
}
}) ;
}
});
}
} else {
this .recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleFile() ;
}
}接着调用recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleFile:
private void recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleFile() {
this.recreateReactContextInBackground(new com.facebook.react.bridge.JSCJavaScriptExecutor.Factory(), JSBundleLoader.createFileLoader(this.mApplicationContext, this.mJSBundleFile));
}经过1系列的周转,最后调用到了recreateReactContextInBackground:
private void recreateReactContextInBackground(com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptExecutor.Factory jsExecutorFactory, JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader) {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.ReactContextInitParams initParams = new ReactInstanceManagerImpl.ReactContextInitParams(jsExecutorFactory , jsBundleLoader);
if( this.mReactContextInitAsyncTask == null) {
this .mReactContextInitAsyncTask = new ReactInstanceManagerImpl.ReactContextInitAsyncTask( null);
this.mReactContextInitAsyncTask.execute( new ReactInstanceManagerImpl.ReactContextInitParams[]{initParams}) ;
} else {
this .mPendingReactContextInitParams = initParams ;
}
}上面代码通过ReactContextInitAsyncTask这个AsyncTask来初始化ReactCotext。
private final class ReactContextInitAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<ReactInstanceManagerImpl.ReactContextInitParams, Void, ReactInstanceManagerImpl.Result<ReactApplicationContext>> {
private ReactContextInitAsyncTask() {
}
protected void onPreExecute() {
if(ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mCurrentReactContext != null) {
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.tearDownReactContext(ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mCurrentReactContext);
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mCurrentReactContext = null;
}
}
protected ReactInstanceManagerImpl.Result<ReactApplicationContext> doInBackground(ReactInstanceManagerImpl.ReactContextInitParams... params) {
Assertions.assertCondition(params != null && params.length > 0 && params[0] != null);
try {
JavaScriptExecutor e = params[0].getJsExecutorFactory().create(ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mJSCConfig == null?new WritableNativeMap():ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mJSCConfig.getConfigMap());
return ReactInstanceManagerImpl.Result.of((Object)ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.createReactContext(e, params[0].getJsBundleLoader()));
} catch (Exception var3) {
return ReactInstanceManagerImpl.Result.of(var3);
}
}
protected void onPostExecute(ReactInstanceManagerImpl.Result<ReactApplicationContext> result) {
try {
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.setupReactContext((ReactApplicationContext)result.get());
} catch (Exception var6) {
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mDevSupportManager.handleException(var6);
} finally {
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mReactContextInitAsyncTask = null;
}
if(ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mPendingReactContextInitParams != null) {
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.recreateReactContextInBackground(ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mPendingReactContextInitParams.getJsExecutorFactory(), ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mPendingReactContextInitParams.getJsBundleLoader());
ReactInstanceManagerImpl.this.mPendingReactContextInitParams = null;
}
}ReactContextInitAsyncTask为创建ReactContext的核心类,随后,调用createReactContext进1步创建ReactContext。在创建完React Context后会调用setUpReactContext,将ReactRootView做为Root View传递给UIManagerModule,调用AppRegistry的runApplication去启动Js Application等。看createReactContext的代码:
private ReactApplicationContext createReactContext(JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor , JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader) {
FLog.i("React" , "Creating react context.");
ReactMarker.logMarker( "CREATE_REACT_CONTEXT_START" );
this.mSourceUrl = jsBundleLoader.getSourceUrl() ;
Builder nativeRegistryBuilder = new Builder();
com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptModulesConfig.Builder jsModulesBuilder = new com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptModulesConfig.Builder() ;
ReactApplicationContext reactContext = new ReactApplicationContext( this.mApplicationContext);
if( this.mUseDeveloperSupport) {
reactContext.setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler(this.mDevSupportManager) ;
}
ReactMarker.logMarker("PROCESS_PACKAGES_START" );
Systrace.beginSection( 0L, "createAndProcessCoreModulesPackage" );
try {
CoreModulesPackage nativeModuleRegistry = new CoreModulesPackage( this, this.mBackBtnHandler , this.mUIImplementationProvider);
this.processPackage(nativeModuleRegistry , reactContext, nativeRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder) ;
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L );
}
Iterator nativeModuleRegistry2 = this .mPackages.iterator();
while(nativeModuleRegistry2.hasNext()) {
ReactPackage javaScriptModulesConfig = (ReactPackage)nativeModuleRegistry2.next();
Systrace.beginSection( 0L, "createAndProcessCustomReactPackage" );
try {
this .processPackage(javaScriptModulesConfig , reactContext, nativeRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder) ;
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L) ;
}
}
ReactMarker.logMarker("PROCESS_PACKAGES_END" );
ReactMarker.logMarker( "BUILD_NATIVE_MODULE_REGISTRY_START" );
Systrace.beginSection( 0L, "buildNativeModuleRegistry" );
NativeModuleRegistry nativeModuleRegistry1 ;
try {
nativeModuleRegistry1 = nativeRegistryBuilder.build();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L );
ReactMarker.logMarker( "BUILD_NATIVE_MODULE_REGISTRY_END" );
}
ReactMarker.logMarker("BUILD_JS_MODULE_CONFIG_START" );
Systrace.beginSection( 0L, "buildJSModuleConfig" );
JavaScriptModulesConfig javaScriptModulesConfig1 ;
try {
javaScriptModulesConfig1 = jsModulesBuilder.build();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L );
ReactMarker.logMarker( "BUILD_JS_MODULE_CONFIG_END" );
}
Object exceptionHandler = this .mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler != null?this .mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler: this.mDevSupportManager;
com.facebook.react.bridge.CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder catalystInstanceBuilder = ( new com.facebook.react.bridge.CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder()).setReactQueueConfigurationSpec(ReactQueueConfigurationSpec.createDefault()).setJSExecutor(jsExecutor).setRegistry(nativeModuleRegistry1).setJSModulesConfig(javaScriptModulesConfig1).setJSBundleLoader(jsBundleLoader).setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler((NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler)exceptionHandler) ;
ReactMarker.logMarker( "CREATE_CATALYST_INSTANCE_START" );
Systrace.beginSection( 0L, "createCatalystInstance" );
CatalystInstanceImpl catalystInstance ;
try {
catalystInstance = catalystInstanceBuilder.build();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L );
ReactMarker.logMarker( "CREATE_CATALYST_INSTANCE_END" );
}
if (this.mBridgeIdleDebugListener != null) {
catalystInstance.addBridgeIdleDebugListener(this.mBridgeIdleDebugListener) ;
}
reactContext.initializeWithInstance(catalystInstance);
ReactMarker.logMarker( "RUN_JS_BUNDLE_START" );
Systrace.beginSection( 0L, "runJSBundle" );
try {
catalystInstance.runJSBundle();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L );
ReactMarker.logMarker( "RUN_JS_BUNDLE_END" );
}
return reactContext;
}代码很长,我们来分段分析。
第1步
com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptModulesConfig.Builder jsModulesBuilder = new com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptModulesConfig.Builder();创建JavaScriptModulesConfig。
第2步
ReactApplicationContext reactContext = new ReactApplicationContext(this.mApplicationContext);创建ReactApplicationContext上下文。
第3步
try {
CoreModulesPackage nativeModuleRegistry = new CoreModulesPackage(this, this.mBackBtnHandler, this.mUIImplementationProvider);
this.processPackage(nativeModuleRegistry, reactContext, nativeRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
}
Iterator nativeModuleRegistry2 = this.mPackages.iterator();
while(nativeModuleRegistry2.hasNext()) {
ReactPackage javaScriptModulesConfig = (ReactPackage)nativeModuleRegistry2.next();
Systrace.beginSection(0L, "createAndProcessCustomReactPackage");
try {
this.processPackage(javaScriptModulesConfig, reactContext, nativeRegistryBuilder, jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
}
}创建ReactPackage。ReactPackage主要通过createNativeModules、createJSModules和createViewManagers等API去创建本地模块,JS模块及视图组件等。ReactPackage分为framework的CoreModulesPackage和业务方可选的基础MainReactPackage,CoreModulesPackage封装了大部份通讯,调试核心类,如UIManagerModule,这个负责控制Js层Dom到Native View的核心类;看下processPackage方法:
private void processPackage(ReactPackage reactPackage, ReactApplicationContext reactContext, Builder nativeRegistryBuilder, com.facebook.react.bridge.JavaScriptModulesConfig.Builder jsModulesBuilder) {
Iterator i$ = reactPackage.createNativeModules(reactContext).iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
NativeModule jsModuleClass = (NativeModule)i$.next();
nativeRegistryBuilder.add(jsModuleClass);
}
i$ = reactPackage.createJSModules().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Class jsModuleClass1 = (Class)i$.next();
jsModulesBuilder.add(jsModuleClass1);
}
}很简单,拿到具体的native和JS的module把它们添加到对应的builder中。先是添加CoreModulesPackage中的module再添加我们自定义的module,先看CoreModulesPackage中的createNativeModules方法:
public List<NativeModule> createNativeModules(ReactApplicationContext catalystApplicationContext) {
Systrace.beginSection(0L, "createUIManagerModule");
UIManagerModule uiManagerModule;
try {
List viewManagersList = this.mReactInstanceManager.createAllViewManagers(catalystApplicationContext);
uiManagerModule = new UIManagerModule(catalystApplicationContext, viewManagersList, this.mUIImplementationProvider.createUIImplementation(catalystApplicationContext, viewManagersList));
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
}
return Arrays.asList(new NativeModule[]{new AnimationsDebugModule(catalystApplicationContext, this.mReactInstanceManager.getDevSupportManager().getDevSettings()), new AndroidInfoModule(), new DeviceEventManagerModule(catalystApplicationContext, this.mHardwareBackBtnHandler), new ExceptionsManagerModule(this.mReactInstanceManager.getDevSupportManager()), new Timing(catalystApplicationContext), new SourceCodeModule(this.mReactInstanceManager.getSourceUrl(), this.mReactInstanceManager.getDevSupportManager().getSourceMapUrl()), uiManagerModule, new DebugComponentOwnershipModule(catalystApplicationContext)});
}就是将UIManagerModule、AnimationsDebugModule等装到build中。
接着添加我们自定义的组件,以自定义Log为例,需要以下内容吗:
public class AppReactPackage implements ReactPackage{
@Override
public List<NativeModule> createNativeModules(ReactApplicationContext reactApplicationContext) {
List<NativeModule> modules=new ArrayList<>();
modules.add(new LogModule(reactApplicationContext));
return modules;
}
@Override
public List<Class<? extends JavaScriptModule>> createJSModules() {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
@Override
public List<ViewManager> createViewManagers(ReactApplicationContext reactApplicationContext) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}很简单,装到自定义的List中。
第4步
CatalystInstanceImpl catalystInstance;
try {
catalystInstance = catalystInstanceBuilder.build();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
ReactMarker.logMarker("CREATE_CATALYST_INSTANCE_END");
}创建CatalystInstance。CatalystInstance其实不直接面向开发者,开发者通ReactInstanceManger间接操作CatalystInstance。CatalystInstance持有对ReactBridge的援用,主要通过ReactBridge这个JNI类去实现Java层与Js层的通讯,ReactBridge由CatalystInstance的Constructor创建。同时初始化的时候调用了ReactQueueConfigurationSpec.createDefault创建了ReactNative通讯的两个线程 JsQueueThread&NativeModulesQueueThread;
在这里ReactBridge由CatalystInstance的Constructor创建。看下它的构造函数:
private CatalystInstanceImpl(ReactQueueConfigurationSpec ReactQueueConfigurationSpec, final JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor, NativeModuleRegistry registry, final JavaScriptModulesConfig jsModulesConfig, JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader, NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler nativeModuleCallExceptionHandler) {
this.mPendingJSCalls = new AtomicInteger(0);
this.mJsPendingCallsTitleForTrace = "pending_js_calls_instance" + sNextInstanceIdForTrace.getAndIncrement();
this.mDestroyed = false;
this.mJSToJavaCallsTeardownLock = new Object();
this.mJavaToJSCallsTeardownLock = new Object();
this.mInitialized = false;
FLog.d("React", "Initializing React Bridge.");
this.mReactQueueConfiguration = ReactQueueConfigurationImpl.create(ReactQueueConfigurationSpec, new CatalystInstanceImpl.NativeExceptionHandler(null));
this.mBridgeIdleListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList();
this.mJavaRegistry = registry;
this.mJSModuleRegistry = new JavaScriptModuleRegistry(this, jsModulesConfig);
this.mJSBundleLoader = jsBundleLoader;
this.mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler = nativeModuleCallExceptionHandler;
this.mTraceListener = new CatalystInstanceImpl.JSProfilerTraceListener(null);
try {
this.mBridge = (ReactBridge)this.mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread().callOnQueue(new Callable() {
public ReactBridge call() throws Exception {
Systrace.beginSection(0L, "initializeBridge");
ReactBridge var1;
try {
var1 = CatalystInstanceImpl.this.initializeBridge(jsExecutor, jsModulesConfig);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
}
return var1;
}
}).get();
} catch (Exception var8) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize bridge", var8);
}
}注意到这行代码:
this.mJSModuleRegistry = new JavaScriptModuleRegistry(this, jsModulesConfig);这里通过jsModulesConfig(封装了module)创建了JSModuleRegistry。好了js注册表终究创建成功了。这里有两个问题,native注册表在哪创建呢,还有就是注册表甚么时候传给js层呢。先留着这两个问题。
接下来看下initializeBridge方法:
private ReactBridge initializeBridge (JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor, JavaScriptModulesConfig jsModulesConfig) {
this .mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread().assertIsOnThread() ;
Assertions.assertCondition( this.mBridge == null, "initializeBridge should be called once" );
Systrace.beginSection( 0L, "ReactBridgeCtor" );
ReactBridge bridge ;
try {
bridge = new ReactBridge(jsExecutor, new CatalystInstanceImpl.NativeModulesReactCallback( null), this.mReactQueueConfiguration.getNativeModulesQueueThread()) ;
this.mMainExecutorToken = bridge.getMainExecutorToken() ;
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L );
}
Systrace.beginSection(0L , "setBatchedBridgeConfig");
try {
bridge.setGlobalVariable("__fbBatchedBridgeConfig" , this.buildModulesConfigJSONProperty( this.mJavaRegistry, jsModulesConfig));
bridge.setGlobalVariable( "__RCTProfileIsProfiling" , Systrace.isTracing( 0L)?"true" :"false") ;
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L );
}
this .mJavaRegistry.notifyReactBridgeInitialized(bridge) ;
return bridge ;
}ReactBridge将注册表信息存入与前端互通的全局变量 __fbBatchedBridgeConfig 中,使得Js层与Java层存在一样的模块注册表。bridge.setGlobalVariable是1个native函数。让我们猜1下下它的功能,就是用jsModulesConfig这个参数在js层中生成模块注册表,先看1下参数 buildModulesConfigJSONProperty的代码:
private String buildModulesConfigJSONProperty(NativeModuleRegistry nativeModuleRegistry, JavaScriptModulesConfig jsModulesConfig) {
StringWriter stringWriter = new StringWriter();
JsonWriter writer = new JsonWriter(stringWriter);
String ioe;
try {
writer.beginObject();
writer.name("remoteModuleConfig");
nativeModuleRegistry.writeModuleDescriptions(writer);
writer.name("localModulesConfig");
jsModulesConfig.writeModuleDescriptions(writer);
writer.endObject();
ioe = stringWriter.toString();
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to serialize JavaScript module declaration", var14);
} finally {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException var13) {
;
}
}
return ioe;
}看到JsonWriter就知道是把NativeModuleRegistry 和JavaScriptModulesConfig 转换成Json字符串,其中remoteModuleConfig指NativeModuleRegistry 信息,localModulesConfig指JavaScriptModulesConfig 信息。看下JavaScriptModulesConfig 的writeModuleDescriptions方法:
public void writeModuleDescriptions(JsonWriter writer) throws IOException {
writer.beginObject();
Iterator i$ = this.mModules.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
JavaScriptModuleRegistration registration = (JavaScriptModuleRegistration)i$.next();
writer.name(registration.getName()).beginObject();
this.appendJSModuleToJSONObject(writer, registration);
writer.endObject();
}
writer.endObject();
}看下appendJSModuleToJSONObject方法:
private void appendJSModuleToJSONObject(JsonWriter writer, JavaScriptModuleRegistration registration) throws IOException {
writer.name("moduleID").value((long)registration.getModuleId());
writer.name("methods").beginObject();
Iterator i$ = registration.getMethods().iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
Method method = (Method)i$.next();
writer.name(method.getName()).beginObject();
writer.name("methodID").value((long)registration.getMethodId(method));
writer.endObject();
}
writer.endObject();
if(registration.getModuleInterface().isAnnotationPresent(SupportsWebWorkers.class)) {
writer.name("supportsWebWorkers").value(true);
}
}从上代码可知生成的json字符串包括moduleID和methodID信息。NativeModuleRegistry 也同理,我们大概看下它的代码:
void writeModuleDescriptions(JsonWriter writer) throws IOException {
Systrace.beginSection(0L, "CreateJSON");
try {
writer.beginObject();
Iterator i$ = this.mModuleTable.iterator();
while(i$.hasNext()) {
NativeModuleRegistry.ModuleDefinition moduleDef = (NativeModuleRegistry.ModuleDefinition)i$.next();
writer.name(moduleDef.name).beginObject();
writer.name("moduleID").value((long)moduleDef.id);
writer.name("supportsWebWorkers").value(moduleDef.target.supportsWebWorkers());
writer.name("methods").beginObject();
for(int i = 0; i < moduleDef.methods.size(); ++i) {
NativeModuleRegistry.MethodRegistration method = (NativeModuleRegistry.MethodRegistration)moduleDef.methods.get(i);
writer.name(method.name).beginObject();
writer.name("methodID").value((long)i);
writer.name("type").value(method.method.getType());
writer.endObject();
}
writer.endObject();
moduleDef.target.writeConstantsField(writer, "constants");
writer.endObject();
}
writer.endObject();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
}
}
接下来我们要找到setGlobalVariable的Native层代码,C++层代码我不太懂,这里参考了下他人的分析进程。大概进程是这样,首先入口是OnLoad.cpp。在其中找到以下代码:
void Bridge::setGlobalVariable(const std::string& propName, const std::string& jsonValue) {
runOnExecutorQueue(*m_mainExecutorToken, [=] (JSExecutor* executor) {
executor->setGlobalVariable(propName, jsonValue);
});
}
都是塞进runOnExecutorQueue履行队列里面等待调用,最后回调到JSExecutor,而JSExecutor的实现类是JSCExecutor,最后来看看它的setGlobalVariable方法。
void JSCExecutor::setGlobalVariable(const std::string& propName, const std::string& jsonValue) {
auto globalObject = JSContextGetGlobalObject(m_context);
String jsPropertyName(propName.c_str());
String jsValueJSON(jsonValue.c_str());
auto valueToInject = JSValueMakeFromJSONString(m_context, jsValueJSON);
JSObjectSetProperty(m_context, globalObject, jsPropertyName, valueToInject, 0, NULL);
}懂个大概吧,参数propName是从Java层传递过来的,相当于java代码中的__fbBatchedBridgeConfig和__RCTProfileIsProfiling。jsPropertyName方法就是buildModulesConfigJSONProperty封装好的对象。JSContextGetGlobalObject是WeiKit的方法,接下来会调用到js层的MessageQueue中:
const MessageQueue = require('MessageQueue');
const BatchedBridge = new MessageQueue(
__fbBatchedBridgeConfig.remoteModuleConfig,
__fbBatchedBridgeConfig.localModulesConfig,
);生成两个映照表,从上面的代码我们己经分析过了,remoteModuleConfig是NativeModuleRegisty映照表内容。localModulesConfig则是JavaScriptModule内容。
到这里,js就生成了两张映照表了,这样java层和js层就都存在一样的映照表,相互通讯就是通过它来实现。扯远了,回到createReactView。
第5步
try {
catalystInstance.runJSBundle();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
ReactMarker.logMarker("RUN_JS_BUNDLE_END");
}调用catalystInstance.runJSBundle加载解析Jsbundle。
回到createReactView方法,看catalystInstance.runJSBundle:
public void runJSBundle() {
try {
this.mJSBundleHasLoaded = ((Boolean)this.mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread().callOnQueue(new Callable() {
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
Assertions.assertCondition(!CatalystInstanceImpl.this.mJSBundleHasLoaded, "JS bundle was already loaded!");
CatalystInstanceImpl.this.incrementPendingJSCalls();
Systrace.beginSection(0L, "loadJSScript");
try {
CatalystInstanceImpl.this.mJSBundleLoader.loadScript(CatalystInstanceImpl.this.mBridge);
Systrace.registerListener(CatalystInstanceImpl.this.mTraceListener);
} catch (JSExecutionException var5) {
CatalystInstanceImpl.this.mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler.handleException(var5);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
}
return Boolean.valueOf(true);
}
}).get()).booleanValue();
} catch (Exception var2) {
throw new RuntimeException(var2);
}
}调用catalystInstance.runJSBundle加载解析Jsbundle。假设在解析进程中出现Exception,统1交给NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler处理。
在创建完React Context后会履行ReactContextInitAsyncTask的onPostExecute。来看下onPostExecute的代码:
private void setupReactContext(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
Assertions.assertCondition(this.mCurrentReactContext == null);
this.mCurrentReactContext = (ReactContext)Assertions.assertNotNull(reactContext);
CatalystInstance catalystInstance = (CatalystInstance)Assertions.assertNotNull(reactContext.getCatalystInstance());
catalystInstance.initialize();
this.mDevSupportManager.onNewReactContextCreated(reactContext);
this.mMemoryPressureRouter.addMemoryPressureListener(catalystInstance);
this.moveReactContextToCurrentLifecycleState();
Iterator listeners = this.mAttachedRootViews.iterator();
while(listeners.hasNext()) {
ReactRootView arr$ = (ReactRootView)listeners.next();
this.attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance(arr$, catalystInstance);
}
ReactInstanceEventListener[] var8 = new ReactInstanceEventListener[this.mReactInstanceEventListeners.size()];
var8 = (ReactInstanceEventListener[])this.mReactInstanceEventListeners.toArray(var8);
ReactInstanceEventListener[] var9 = var8;
int len$ = var8.length;
for(int i$ = 0; i$ < len$; ++i$) {
ReactInstanceEventListener listener = var9[i$];
listener.onReactContextInitialized(reactContext);
}
}这里主要实现两个功能,第1,调用catalystInstance.initialize()来创建NativeModuleRegistry,好啦,回答了1个问题了哈。
public void initialize() {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
Assertions.assertCondition(!this.mInitialized, "This catalyst instance has already been initialized");
this.mInitialized = true;
this.mJavaRegistry.notifyCatalystInstanceInitialized();
}第2,调用attachMeasuredRootView方法。将ReactRootView做为Root View传递给UIManagerModule,尔后Js通过UIManager创建的View都会add到该View上。以下:
public void attachMeasuredRootView(ReactRootView rootView) {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
this.mAttachedRootViews.add(rootView) ;
if( this.mReactContextInitAsyncTask == null && this.mCurrentReactContext != null) {
this .attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance(rootView , this.mCurrentReactContext.getCatalystInstance()) ;
}
}再来看下attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance这个方法:
private void attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance(ReactRootView rootView , C