前言:有人问我,即使梦想成真了又能怎样,也许不能怎样,但这是梦想。
相干文章:
1、《PopUpWindow使用详解(1)――基本使用》
2、《PopUpWindow使用详解(2)――进阶及答疑》
上篇为大家基本讲述了有关PopupWindow的基本使用,但还有几个相干函数还没有讲述,我们这篇将侧重看看这几个函数的用法并结合源码来说讲具体缘由,最后是有关PopupWindow在使用时的疑问,给大家讲授1下。
1、经常使用函数讲授
这段将会给大家讲下下面几个函数的意义及用法,使用上篇那个带背景的例子为基础。
public void setTouchable(boolean touchable)
public void setFocusable(boolean focusable)
public void setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)
public void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background)
1、setTouchable(boolean touchable)
设置PopupWindow是不是响应touch事件,默许是true,如果设置为false,即会是下面这个结果:(所有touch事件无响应,包括点击事件)
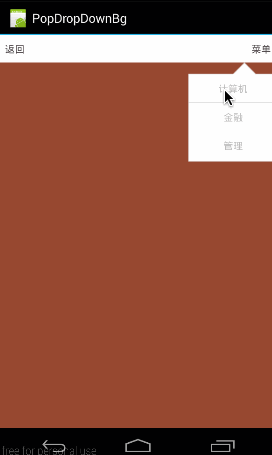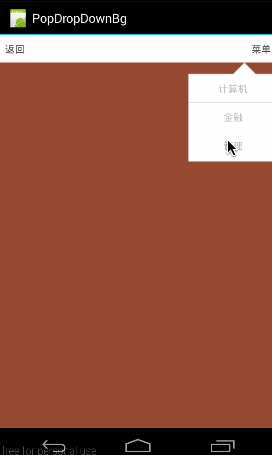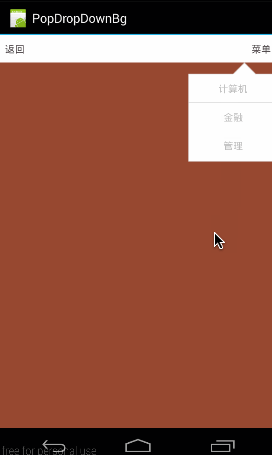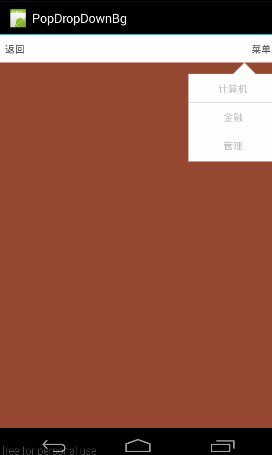
对应代码:
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setTouchable(false);
………………//单项点击
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
2、setFocusable(boolean focusable)
该函数的意义表示,PopupWindow是不是具有获得焦点的能力,默许为False。1般来说是没有用的,由于普通的控件是不需要获得焦点的,而对EditText则不同,如果不能获得焦点,那末EditText将是没法编辑的。
所以,我们在popuplayout.xml最底部添加1个EditText,分别演示两段不同的代码,即分别将setFocusable设置为false和设置为true;看看有甚么不同:
(1)setFocusable(true)代码以下:
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
//是不是具有获得焦点的能力
mPopWindow.setFocusable(true);
…………//各item点击响应
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
明显在点击EditText的时候,会弹出编辑框。
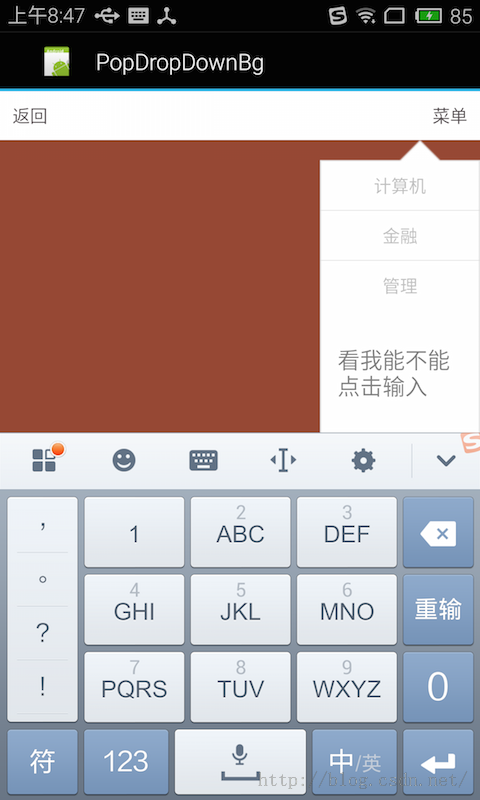
(2)setFocusable(false)
一样上面1段代码,那我们将setFocusable设置为false,会是怎样呢?
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
//是不是具有获得焦点的能力
mPopWindow.setFocusable(false);
…………//各item点击响应
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
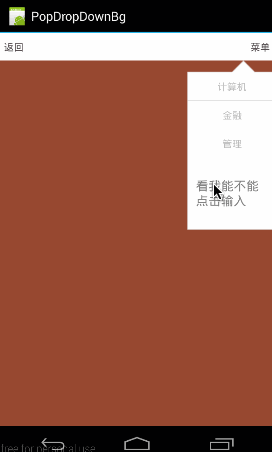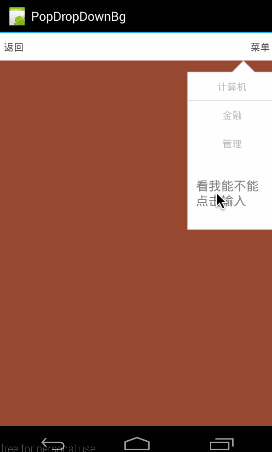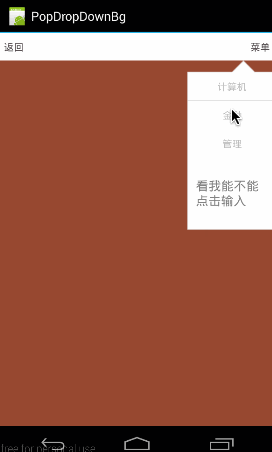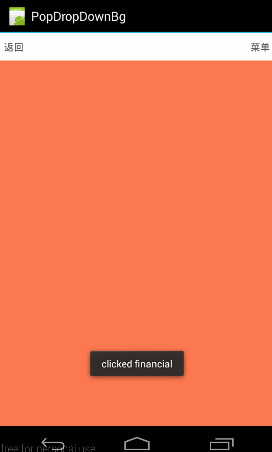
效果图下:
可见,点击EditText没有出现任何反应!所以如果PopupWindow没有获得焦点的能力,那末它其中的EditText固然是没办法获得焦点的,EditText没法获得焦点,那对它而言全部EditText控件就是不可用的。
3、setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)
这个函数的意义,就是指,PopupWindow之外的区域是不是可点击,即如果点击PopupWindow之外的区域,PopupWindow是不是会消失。
下面这个是点击会消息的效果图:

看看它对应的代码:
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
//外部是不是可以点击
mPopWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(new BitmapDrawable());
mPopWindow.setOutsideTouchable(true);
…………//各ITEM点击响应
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
这里要非常注意的1点:
mPopWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(new BitmapDrawable());
mPopWindow.setOutsideTouchable(true);
大家可能要疑问,为何要加上mPopWindow.setBackgroundDrawable(new BitmapDrawable());这句呢,从代码来看没并没有真正设置Bitmap,而只是new了1个空的bitmap,好像并没起到甚么作用。那如果我们把这句去掉会怎样:
把代码改成这模样:(只使用setOutsideTouchable)
private void showPopupWindow() {
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
//外部是不是可以点击
mPopWindow.setOutsideTouchable(true);
…………//各ITEM点击响应
mPopWindow.showAsDropDown(mMenuTv);
}
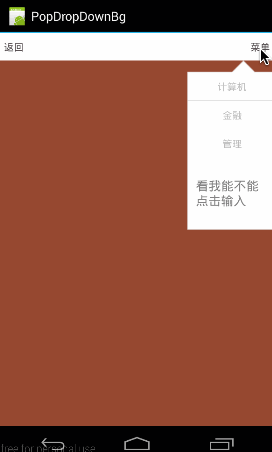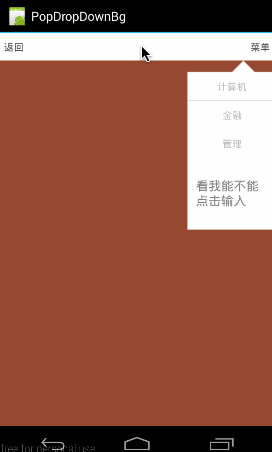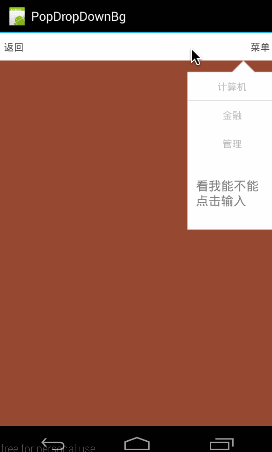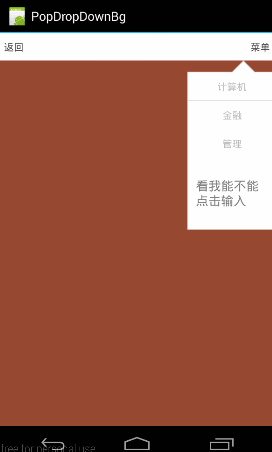
看到了没,点击外部没反应………………这就有点坑了,至于缘由,我们在setBackgroundDrawable()中讲。
4、setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background)
这个函数可是吊了,这个函数不只能设置背景……,由于你加上它以后,setOutsideTouchable()才会生效;
而且,只有加上它以后,PopupWindow才会对手机的返回按钮有响应:即,点击手机返回按钮,可以关闭PopupWindow;如果不加setBackgroundDrawable()将关闭的PopupWindow所在的Activity.
这个函数要怎样用,这里应当就不用讲了吧,可以填充进去各种Drawable,比如new BitmapDrawable(),new ColorDrawable(),等;
我们这里主要从源码的角度来看看setBackgroundDrawable()后,PopupWindow都做了些甚么。
首先看看setBackgroundDrawable(),将传进去的background赋值给mBackground;
void setBackgroundDrawable(Drawable background) {
mBackground = background;
}
然后再看看显示showAsDropDown()显示的时候,都做了些甚么。代码以下:
public void showAsDropDown(View anchor, int xoff, int yoff) {
…………
//准备窗口
WindowManager.LayoutParams p = createPopupLayout(anchor.getWindowToken());
preparePopup(p);
…………
//显示窗口
invokePopup(p);
}
在这段代码中,先是准备窗口用来显示,然后再利用invokePopup()来显示窗体。
我们看看在preparePopup(p)中是怎样准备窗体的:
private void preparePopup(WindowManager.LayoutParams p) {
if (mBackground != null) {
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = mContentView.getLayoutParams();
int height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
if (layoutParams != null &&
layoutParams.height == ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
height = ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
// when a background is available, we embed the content view
// within another view that owns the background drawable
PopupViewContainer popupViewContainer = new PopupViewContainer(mContext);
PopupViewContainer.LayoutParams listParams = new PopupViewContainer.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, height
);
popupViewContainer.setBackgroundDrawable(mBackground);
popupViewContainer.addView(mContentView, listParams);
mPopupView = popupViewContainer;
} else {
mPopupView = mContentView;
}
mPopupWidth = p.width;
mPopupHeight = p.height;
}
从上面可以看出,如果mBackground不这空,会首先生成1个PopupViewContainer的ViewContainer,然后把mContentView做为子布局add进去,然后把popupViewContainer做为PopupWindow做为根布局。
popupViewContainer.addView(mContentView, listParams);
那如果mBackground不为空,那就直接把mContentView做为View传递给PopupWindow窗体。
mPopupView = mContentView
到此,我们知道,如果mBackground不为空,会在我们设置的contentView外再包1层布局。那下面,我们再看看包的这层布局都干了甚么:
先列出来完全的代码,然后再分步讲(已做精简,如需知道更多,可参看源码)
private class PopupViewContainer extends FrameLayout {
private static final String TAG = "PopupWindow.PopupViewContainer";
public PopupViewContainer(Context context) {
super(context);
}
…………
@Override
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
if (event.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) {
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
…………
} else if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {
KeyEvent.DispatcherState state = getKeyDispatcherState();
if (state != null && state.isTracking(event) && !event.isCanceled()) {
dismiss();
return true;
}
}
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
} else {
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final int x = (int) event.getX();
final int y = (int) event.getY();
if ((event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN)
&& ((x < 0) || (x >= getWidth()) || (y < 0) || (y >= getHeight()))) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else {
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
…………
}
这里总共需要注意3部份:(1)、PopupViewContainer派生自FrameLayout从PopupViewContainer声明上可以看到,PopupViewContainer派生自FrameLayout;所以,这也是它能将我们传进来的contentView添加为自己的子布局的缘由。
(2)、返回按钮捕捉public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
if (event.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK) {
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& event.getRepeatCount() == 0) {
…………
} else if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {
//抬起手指时
KeyEvent.DispatcherState state = getKeyDispatcherState();
if (state != null && state.isTracking(event) && !event.isCanceled()) {
//隐藏窗体
dismiss();
return true;
}
}
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
} else {
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event);
}
}
从上面的代码来看,PopupViewContainer捕捉了KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK事件,并且在用户在点击back按钮,抬起手指的时候(event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP)将窗体隐藏掉。
所以,添加上mBackground以后,可以在用户点击返回按钮时,隐藏窗体!
(3)、捕捉Touch事件――onTouchEventpublic boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final int x = (int) event.getX();
final int y = (int) event.getY();
if ((event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN)
&& ((x < 0) || (x >= getWidth()) || (y < 0) || (y >= getHeight()))) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else {
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
从这代码来看,PopupViewContainer捕捉了两种touch事件,MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN和MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE;将接收到这两个事件时,会将窗体隐藏掉。
MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN的触发很好理解,即当用户点击到PopupViewContainer事件时,就隐藏掉;
所以,下面的情况就来了:
假设有1个TextView,我们没有对它设置点击响应。那只要加了background,那点击事件就会传给下层的PopupViewContainer,从而使窗体消失。
那还有个问题,MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE是个甚么鬼?它是怎样触发的。我们在下面开1段细讲。
(4)MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE与setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)可能把这两个放在1块,大家可能就恍然大悟了,表着急,1个个来看。
先看看setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable)的代码:
public void setOutsideTouchable(boolean touchable) {
mOutsideTouchable = touchable;
}
然后再看看mOutsideTouchable哪里会用到
下面代码,我做了严重精减,等下会再完全再讲这1块
private int computeFlags(int curFlags) {
curFlags &= ~(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH);
…………
if (mOutsideTouchable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH;
}
…………
return curFlags;
}
这段代码主要是用各种变量来设置window所使用的flag;
首先,将curFlags所在运算的各种Flag,全部置为False;代码以下:
curFlags &= ~(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH);
然后,再根据用户设置的变量来开启:
if (mOutsideTouchable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH;
}
既然讲到FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH,那我们来看看FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH所代表的意义:
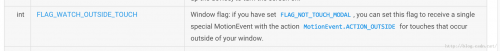
这段话的意思是说,如果窗体设置了FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH这个flag,那末 用户点击窗体之外的位置时,将会在窗体的MotionEvent中收到MotionEvetn.ACTION_OUTSIDE事件。
参见:《WindowManager.LayoutParams》
所以在PopupViewContainer中添加了对MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE的捕捉!当用户点击PopupViewContainer之外的区域时,将dismiss掉PopupWindow
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
final int x = (int) event.getX();
final int y = (int) event.getY();
if ((event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN)
&& ((x < 0) || (x >= getWidth()) || (y < 0) || (y >= getHeight()))) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE) {
dismiss();
return true;
} else {
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
}
(5)重看PopupWindow的computeFlags(int curFlags)函数完全的computeFlags()函数以下:
private int computeFlags(int curFlags) {
curFlags &= ~(
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_IGNORE_CHEEK_PRESSES |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCHABLE |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_NO_LIMITS |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_ALT_FOCUSABLE_IM |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH);
if(mIgnoreCheekPress) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_IGNORE_CHEEK_PRESSES;
}
if (!mFocusable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE;
if (mInputMethodMode == INPUT_METHOD_NEEDED) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_ALT_FOCUSABLE_IM;
}
} else if (mInputMethodMode == INPUT_METHOD_NOT_NEEDED) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_ALT_FOCUSABLE_IM;
}
if (!mTouchable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCHABLE;
}
if (mOutsideTouchable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH;
}
if (!mClippingEnabled) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_NO_LIMITS;
}
if (isSplitTouchEnabled()) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH;
}
if (mLayoutInScreen) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN;
}
if (mLayoutInsetDecor) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR;
}
if (mNotTouchModal) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCH_MODAL;
}
return curFlags;
}
这段代码一样是分两段:
第1段:将所有要计算的FLAG,全部在结果curFlags中置为FALSE;
curFlags &= ~(
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_IGNORE_CHEEK_PRESSES |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_FOCUSABLE |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCHABLE |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_LAYOUT_NO_LIMITS |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_ALT_FOCUSABLE_IM |
WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH);
第2段:然后根据用户设置的变量,逐一判断是不是打开。比以下面这个:
//看到了吧,我们的setTouchable(boolean touchable)终究也是通过在这里设置的
if (!mTouchable) {
curFlags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_NOT_TOUCHABLE;
}
好了,结合源码就给大家讲到这里了。最后总结1下:
**如果我们给PopupWindow添加了mBackground,那它将会:**- setOutsideTouchable(true)将生效,具有外部点击隐藏窗体的功能
- 手机上的返回键将可使窗体消失
- 对PopupWindow上层没有捕捉的点击事件,点击以后,依然能使窗体消失。
源码在文章底部给出
2、为何要强迫代码设置PopupWindow的Height、Width
在上篇,我们留了这么个疑问,设置contentView很容易理解,但width和height为何要强迫设置呢?我们在布局代码中不是已写的很清楚了么?比如我们的popuplayout.xml的根布局:
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#66000000">
…………
</RelativeLayout>
从根布局中,我们明明可以看到layout_width我们设置为了"fill_parent",layout_height设置为了“fill_parent”;为何非要我们在代码中还要再设置1遍:
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
mPopWindow = new PopupWindow(contentView);
mPopWindow.setWidth(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
mPopWindow.setHeight(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
带着这个疑问,我们从两个角度来分析,”源码角度”看看就好,关键的解答在第2部份:布局角度;
1、源码角度
首先,我们从源码我角度来分析为何要设置Width和Height;我们就以setWidth()为例来追根寻底下
先看下setWidth():
public void setWidth(int width) {
mWidth = width;
}
然后再看看mWidth在哪里用到:
private WindowManager.LayoutParams createPopupLayout(IBinder token) {
// generates the layout parameters for the drop down
// we want a fixed size view located at the bottom left of the anchor
WindowManager.LayoutParams p = new WindowManager.LayoutParams();
// these gravity settings put the view at the top left corner of the
// screen. The view is then positioned to the appropriate location
// by setting the x and y offsets to match the anchor's bottom
// left corner
p.gravity = Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP;
p.width = mLastWidth = mWidth;
p.height = mLastHeight = mHeight;
if (mBackground != null) {
p.format = mBackground.getOpacity();
} else {
p.format = PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT;
}
p.flags = computeFlags(p.flags);
p.type = mWindowLayoutType;
p.token = token;
p.softInputMode = mSoftInputMode;
p.setTitle("PopupWindow:" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()));
return p;
}
上面是createPopupLayout的完全代码,我们提取1下:
private WindowManager.LayoutParams createPopupLayout(IBinder token) {
…………
p.width = mLastWidth = mWidth;
p.height = mLastHeight = mHeight;
…………
return p;
}
从这里即可以清晰的看到窗体的宽度和高度都是通过mWidth和mHeight来设置的。
那问题来了,mWidth在哪里能设置呢:
通篇代码中,总共只有3个函数能设置mWidth,分别以下:
除setWidth()函数本身,就只有PopupWindow()的两个构造函数了;
public void setWidth(int width) {
mWidth = width;
}
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height) {
this(contentView, width, height, false);
}
public PopupWindow(View contentView, int width, int height, boolean focusable) {
if (contentView != null) {
mContext = contentView.getContext();
mWindowManager = (WindowManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE);
}
setContentView(contentView);
setWidth(width);
setHeight(height);
setFocusable(focusable);
}
那末问题来了,如果我们没有设置width和height那结果会如何呢?
如果我们没有设置width和height,那mWidth和mHeight将会取默许值0!!!!所以当我们没有设置width和height时,其实不是我们的窗体没有弹出来,而是由于他们的width和height都是0了!!!!
**那末问题又来了:Google那帮老头,不能从我们contentView的根布局中取参数吗,非要我们自己设?**固然不是那帮老头的代码有问题,由于这牵涉了更深层次的内容:布局参数的设定问题!我们在下1部份,布局角度来解答。
2、布局角度
这部份我们侧重讲1个问题:控件的布局参数从哪里来?
我们看下面这段XML:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf⑻"?>
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@drawable/pop_bg"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="2dp"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/pop_computer"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
style="@style/pop_text_style"
android:text="计算机"/>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
很明显,这段代码是个3层结构,TextView是终究的子控件。
那我现在要问了:TextView的显示大小是由谁来决定的?
是由它自己的布局layout_width="wrap_content"、layout_height="wrap_content"来决定的吗?
固然不是!!!!它的大小,应当是在它父控件的基础上决定的。即LinearLayout的显示大小肯定了以后,才能肯定TextView的大小。
这好比,如果LinearLayout的大小是全屏的,那TextView的大小就由它自己来决定了,那如果LinearLayout的大小只有1像素呢?那TextView的所显示的大小不管它自己怎样设置,最大也就显示1像素!
所以我们的结论来了:控件的大小,是建立在父控件大小肯定的基础上的。
那一样:LinearLayout的大小肯定是要靠RelativeLayout来决定。
那问题来了:RelativeLayout的大小靠谁决定呢?
固然是它的父控件了。
我们之前讲过ViewTree的概念,即在android中任何1个APP都会有1个根结点,然后它所有的Activity和Fragmentr所对应的布局都会加入到这个ViewTree中;在ViewTree中每个控件是1个结点:
比以下面这个ViewTree(画的很烂……)
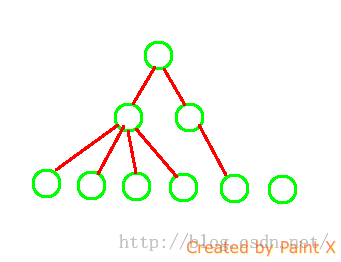
从上面的ViewTree中可以看到,每个结点都是有父结点的(除根结点,根结点不是利用的根结点,与我们利用无关),所以每个控件都是可以找到父控件的的布局大小的。
但我们的contentView是怎样来的呢?
View contentView = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.popuplayout, null);
直接inflate出来的,我们对它没有设置根结点!
那问题来了?它的大小由谁来解决呢?
好像没有谁能决定了,由于他没有父结点。那它究竟是多大呢?未知!
所以只有通过代码让用户去手动设置了!所以这就是为何非要用户设置width和height的缘由了。
好了,到这里,有关PopupWIndow的东东也就讲完了,希望大家能学到东西。
如果本文有帮到你,记得加关注哦
源码下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/harvic880925/9197073
请大家尊重原创者版权,转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/49278705 谢谢
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。






