[置顶] 看数据结构写代码(60 ) 键树的多重链表表示(Trie树)
栏目:综合技术时间:2015-07-29 07:42:17
trie树,是用 树的 多重链表来表示 树的。每一个节点 有 d 个指针域。若从键树中的某个节点到叶子节点的路径上每一个节点都只有1个孩子,则可以把 路径上的所有节点紧缩成1个叶子节点,且在叶子节点中 存储 关键字 和 根关键字相干的信息。
当节点的度 比较大时,选择 Trie树,要比 双链表树更加适合。
tire树的 数据 紧缩 是 挺与众不同的。
下面 给出 具体的 代码:
源代码工程文件网盘地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1cyTg6
// TrieTree.cpp : 定义控制台利用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include "stack.h"
#define BRANCH_MAX_SIZE 27//分支节点最大指针数
#define MAX_SIZE 16
#define LEAF_END_CHAR '$'
enum E_Kind{
E_Kind_Branch,
E_Kind_Leaf,
};
struct KeyType{
char k [MAX_SIZE];
int len;
};
void initKey(KeyType * kt,char *k){
kt->len = strlen(k);
strncpy(kt->k,k,kt->len+1);
}
typedef struct TrieNode{
E_Kind kind;
union {
struct {
TrieNode * ptr[BRANCH_MAX_SIZE];
int num;
}branch;
struct {
char record[MAX_SIZE];
}leaf;
};
}* TrieTree;
TrieNode * makeNode(E_Kind kind){
TrieNode * node = (TrieNode*) malloc(sizeof(TrieNode));
node->kind = kind;
if (kind == E_Kind_Branch){
for (int i = 0; i < BRANCH_MAX_SIZE; i++){
node->branch.ptr[i] = NULL;
}
node->branch.num = 0;
}
return node;
}
TrieNode * makeLeafNode(char * key){
TrieNode * leaf = makeNode(E_Kind_Leaf);
strncpy(leaf->leaf.record,key,strlen(key)+1);
return leaf;
}
void initTree(TrieTree* t){
*t = NULL;
}
void destoryTree(TrieTree * t){
if (*t != NULL)
{
TrieTree p = *t;
if (p->kind == E_Kind_Branch){
for (int i = 0; i < BRANCH_MAX_SIZE; i++){
if (p->branch.ptr[i] != NULL){
destoryTree(&p->branch.ptr[i]);
}
}
}
free(*t);
*t = NULL;
}
}
int getIndex(char * k,int i){
KeyType kt;
initKey(&kt,k);
int index = 0;
if(i != kt.len){
index = kt.k[i] - 'a' + 1;
}
return index;
}
struct Result{
bool isFind;
TrieNode * t;
int index;
};
//找到了返回 保存记录的 叶子节点;
//否则返回插入位置
Result search(TrieTree t,char * k){
KeyType kt;
initKey(&kt,k);
Result r;
for (int i = 0; t && t->kind == E_Kind_Branch && i<= kt.len; i++){
int index = getIndex(k,i);
r.t = t;
r.index = i;
t = t->branch.ptr[index];
}
if (t && t->kind == E_Kind_Leaf && strcmp(t->leaf.record,k) == 0){//节点可以紧缩,所以没有 == kt.len的条件.
r.isFind = true;
r.t = t;
}
else{
r.isFind = false;
}
return r;
}
void insertTree(TrieTree *t,char * key){
if (*t == NULL){
*t = makeNode(E_Kind_Branch);
}
Result r = search(*t,key);
if (r.isFind == false){
int index = getIndex(key,r.index);
TrieTree p = r.t->branch.ptr[index];
TrieNode * leaf = makeLeafNode(key);
if (p == NULL){
r.t->branch.ptr[index] = leaf;
r.t->branch.num ++;
}
else{
TrieTree q = r.t;
int times = r.index+1;
int len = strlen(key);
while (times <= len){//为字符 相同的节点 建立 分支
int index1 = getIndex(key,times);
int index2= getIndex(p->leaf.record,times);
TrieNode * branch = makeNode(E_Kind_Branch);
q->branch.ptr[index] = branch;
if (index1 != index2){
branch->branch.ptr[index1] = leaf;
branch->branch.ptr[index2] = p;
branch->branch.num += 2;
break;
}
else{
branch->branch.num = 1;
q = branch;
index = index1;
times++;
}
}
}
}
}
void deleteTrie(TrieTree * t,char * k){
if(*t != NULL){
linkStack stack;
stackInit(&stack);
stackPush(&stack,*t);
KeyType kt;
initKey(&kt,k);
TrieTree p = *t;
int i = 0;
for (; p && p->kind == E_Kind_Branch && i <= kt.len; i++){
int index = getIndex(k,i);
stackPush(&stack,p);
p = p->branch.ptr[index];
}
if (p && p->kind == E_Kind_Leaf && strcmp(p->leaf.record,k) == 0){
TrieTree brotherNode = NULL;
while (!stackEmpty(stack)){
TrieTree f;
stackPop(&stack,&f);
free(p);
int index = getIndex(k,i);
f->branch.ptr[i] = NULL;
f->branch.num --;
if (f->branch.num == 0){
p = f;
i--;
if (f == *t){//空树了..
free(*t);
*t = NULL;
}
}
else{
break;
}
}
}
else{//没找到
return;
}
}
}
static char testArray[][MAX_SIZE] = {//18 个
"cao","cai","chang","chao","cha","chen",//6
"wen","wang","wu",//3
"zhao",//1
"li","lan","long","liu",//4
"yun","yang",//2
"zha","l",
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
TrieTree root;
initTree(&root);
for (int i = 0; i < 18; i++){
insertTree(&root,testArray[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 18; i++){
char * s = testArray[i];
Result r = search(root,s);
if (r.isFind){
printf("查找%s ,结果为:%s
",s,r.t->leaf.record);
}
else{
printf("查找%s ,未找到
",s);
}
}
destoryTree(&root);
return 0;
}
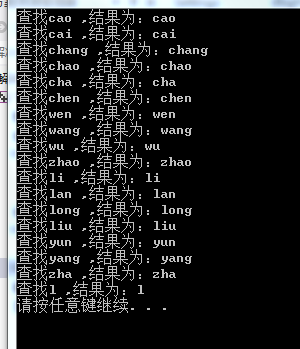
运行截图:
------分隔线----------------------------
------分隔线----------------------------