【计算机视觉】OpenCV人脸识别facerec源码分析2――LBPH概述
人脸辨认
从OpenCV2.4开始,加入了新的类FaceRecognizer,我们可使用它便捷地进行人脸辨认实验。其源代码可以在OpenCV中的opencvmodulescontribdocfacerecsrc下找到。
目前支持的算法有:
Eigenfaces特点脸createEigenFaceRecognizer()
Fisherfaces createFisherFaceRecognizer()
Local Binary Patterns Histograms局部2值直方图 createLBPHFaceRecognizer()
自动人脸辨认就是如何从1幅图象中提取成心义的特点,把它们放入1种有用的表示方式,然后对他们进行1些分类。
特点脸方法描写了1个全面的方法来辨认人脸:脸部图象是1个点,这个点是从高维图象空间找到它在低维空间的表示,这样分类变得很简单。低维子空间低维是使用主元分析(Principal Component Analysis,PCA)找到的,它可以找具有最大方差的那个轴。虽然这样的转换是从最好重建角度斟酌的,但是他没有把标签问题斟酌进去。想象1个情况,如果变化是基于外部来源,比如光照。轴的最大方差不1定包括任何有鉴别性的信息,因此此时的分类是不可能的。因此,1个使用线性鉴别(Linear Discriminant Analysis,LDA)的特定类投影方法被提出来解决人脸辨认问题。其中1个基本的想法就是,使类内方差最小的同时,使类外方差最大。
最近几年来,各种局部特点提取方法出现。为了不输入的图象的高维数据,仅仅使用的局部特点描写图象的方法被提出,提取的特点(很有希望的)对局部遮挡、光照变化、小样本等情况更强健。有关局部特点提取的方法有盖伯小波(Gabor Waelets),离散傅立叶变换(Discrete Cosinus Transform,DCT),局部2值模式(Local Binary Patterns,LBP)。使用甚么方法来提取时域空间的局部特点照旧是1个开放性的研究问题,由于空间信息是潜伏有用的信息。
局部2值模式直方图Local Binary Patterns Histograms
由于Eigenfaces和Fisherfaces两种方法当引入新的人脸数据时需要重新进行训练,所以这里我侧重介绍LBP特点的有关内容。
Eigenfaces和Fisherfaces使用整体方法来进行人脸辨认[gm:直接使用所有的像素]。你把你的数据当作图象空间的高维向量。我们都知道高维数据是糟的,所以1个低维子空间被肯定,对信息保存可能很好。Eigenfaces是最大化总的散度,这样可能致使,当方差由外部条件产生时,最大方差的主成份不合适用来分类。所以为使用1些鉴别分析,我们使用了LDA方法来优化。Fisherfaces方法可以很好的运作,最少在我们假定的模型的有限情况下。
现实生活是不完善的。你没法保证在你的图象中光照条件是完善的,或说1个人的10张照片。所以,如果每人仅仅只有1张照片呢?我们的子空间的协方差估计方法可能完全毛病,所以辨认也可能毛病。
1些研究专注于图象局部特点的提取。主张是我们不把全部图象看成1个高维向量,仅仅用局部特点来描写1个物体。通过这类方式提取特点,你将取得1个低维隐式。1个好主张!但是你很快发现这类图象表示方法不单单遭受光照变化。你想一想图象中的尺度变化、形变、旋转―我们的局部表示方式最少对这些情况比较稳健。正如SIFT,LBP方法在2D纹理分析及第足轻重。LBP的基本思想是对图象的像素和它局部周围像素进行对照后的结果进行求和。把这个像素作为中心,对相邻像素进行阈值比较。如果中心像素的亮度大于等于他的相邻像素,把他标记为1,否则标记为0。你会用2进制数字来表示每一个像素,比如11001111。因此,由于周围相邻8个像素,你终究可能获得2^8个可能组合,被称为局部2值模式,有时被称为LBP码。第1个在文献中描写的LBP算籽实际使用的是3*3的邻域。
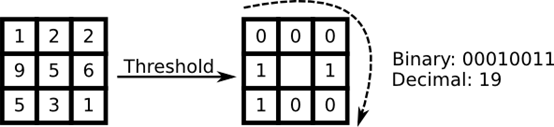
算法描写
1个更加正式的LBP操作可以被定义为:
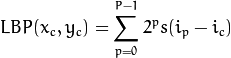
其中(xc,yc)是中心像素,亮度是ic;而in是相邻像素的亮度。s是1个符号函数。
这类描写方法使得你可以很好的捕捉到图象中的细节。实际上,研究者们可以用它在纹理分类上得到最早进的水平。正如刚才描写的方法被提出后,固定的近邻区域对尺度变化的编码失效。所以,使用1个变量的扩大方法是使用可变半径的圆对近邻像素进行编码,这样可以捕捉到以下的近邻:
对1个给定的点(xc,yc),他的近邻点(xp,yp),p∈P可以由以下计算:
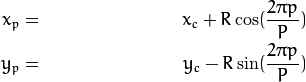
其中,R是圆的半径,而P是样本点的个数。
这个操作是对原始LBP算子的扩大,所以有时被称为扩大LBP(又称为圆形LBP)。如果1个在圆上的点不在图象坐标上,我们使用他的内插点。计算机科学有1堆聪明的插值方法,而OpenCV使用双线性插值。
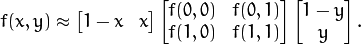
LBP算子,对灰度的单调变化很稳健。我们可以看得手工改变后的图象的LBP图象。

那末剩下来的就是如何合并空间信息用于人脸辨认模型。对LBP图象成m个块,每一个块提取直方图。通过连接局部特直方图(而不是合并)然后就可以得到空间增强的特点向量。这些直方图被称为局部2值模式直方图。
源码分析
LBPH类声明
class LBPH : public FaceRecognizer
{
private:
int _grid_x;
int _grid_y;
int _radius;
int _neighbors;
double _threshold;
vector<Mat> _histograms;
Mat _labels;
// Computes a LBPH model with images in src and
// corresponding labels in labels, possibly preserving
// old model data.
void train(InputArrayOfArrays src, InputArray labels, bool preserveData);
public:
using FaceRecognizer::save;
using FaceRecognizer::load;
// Initializes this LBPH Model. The current implementation is rather fixed
// as it uses the Extended Local Binary Patterns per default.
//
// radius, neighbors are used in the local binary patterns creation.
// grid_x, grid_y control the grid size of the spatial histograms.
LBPH(int radius_=1, int neighbors_=8,
int gridx=8, int gridy=8,
double threshold = DBL_MAX) :
_grid_x(gridx),
_grid_y(gridy),
_radius(radius_),
_neighbors(neighbors_),
_threshold(threshold) {}
// Initializes and computes this LBPH Model. The current implementation is
// rather fixed as it uses the Extended Local Binary Patterns per default.
//
// (radius=1), (neighbors=8) are used in the local binary patterns creation.
// (grid_x=8), (grid_y=8) controls the grid size of the spatial histograms.
LBPH(InputArrayOfArrays src,
InputArray labels,
int radius_=1, int neighbors_=8,
int gridx=8, int gridy=8,
double threshold = DBL_MAX) :
_grid_x(gridx),
_grid_y(gridy),
_radius(radius_),
_neighbors(neighbors_),
_threshold(threshold) {
train(src, labels);
}
~LBPH() { }
// Computes a LBPH model with images in src and
// corresponding labels in labels.
void train(InputArrayOfArrays src, InputArray labels);
// Updates this LBPH model with images in src and
// corresponding labels in labels.
void update(InputArrayOfArrays src, InputArray labels);
// Predicts the label of a query image in src.
int predict(InputArray src) const;
// Predicts the label and confidence for a given sample.
void predict(InputArray _src, int &label, double &dist) const;
// See FaceRecognizer::load.
void load(const FileStorage& fs);
// See FaceRecognizer::save.
void save(FileStorage& fs) const;
// Getter functions.
int neighbors() const { return _neighbors; }
int radius() const { return _radius; }
int grid_x() const { return _grid_x; }
int grid_y() const { return _grid_y; }
AlgorithmInfo* info() const;
};构建LBPH实例
//声明
Ptr<FaceRecognizer> createLBPHFaceRecognizer(int radius=1, int neighbors=8, int grid_x=8, int grid_y=8, double threshold=DBL_MAX);
//定义
Ptr<FaceRecognizer> createLBPHFaceRecognizer(int radius, int neighbors,
int grid_x, int grid_y, double threshold)
{
return new LBPH(radius, neighbors, grid_x, grid_y, threshold);
}参数说明:
* radius :该参数用于构建圆LBP特点。
* neighbors :该参数是构建圆LBP特点所需要的近邻像素的个数,经常使用是8个采样点。采样点越多,计算代价越大。
* grid_x : 该参数是水平方向上划分的格子块个数,常规是8个。区块越多,终究构建结果的特点向量的维度越高。
* grid_y : 该参数是垂直方向上划分的格子块个数,常规是8个。
* threshold : 该阈值用于预测。如果最近邻的距离大于该阈值,预测的方法返回⑴。
LBPH的训练进程
下面给出了LBPH训练函数train的源码,再进行分析。
void LBPH::train(InputArrayOfArrays _in_src, InputArray _in_labels, bool preserveData) {
if(_in_src.kind() != _InputArray::STD_VECTOR_MAT && _in_src.kind() != _InputArray::STD_VECTOR_VECTOR) {
string error_message = "The images are expected as InputArray::STD_VECTOR_MAT (a std::vector<Mat>) or _InputArray::STD_VECTOR_VECTOR (a std::vector< vector<...> >).";
CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message);
}
if(_in_src.total() == 0) {
string error_message = format("Empty training data was given. You'll need more than one sample to learn a model.");
CV_Error(CV_StsUnsupportedFormat, error_message);
} else if(_in_labels.getMat().type() != CV_32SC1) {
string error_message = format("Labels must be given as integer (CV_32SC1). Expected %d, but was %d.", CV_32SC1, _in_labels.type());
CV_Error(CV_StsUnsupportedFormat, error_message);
}
// get the vector of matrices
vector<Mat> src;
_in_src.getMatVector(src);
// get the label matrix
Mat labels = _in_labels.getMat();
// check if data is well- aligned
if(labels.total() != src.size()) {
string error_message = format("The number of samples (src) must equal the number of labels (labels). Was len(samples)=%d, len(labels)=%d.", src.size(), _labels.total());
CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message);
}
// if this model should be trained without preserving old data, delete old model data
if(!preserveData) {
_labels.release();
_histograms.clear();
}
// append labels to _labels matrix
for(size_t labelIdx = 0; labelIdx < labels.total(); labelIdx++) {
_labels.push_back(labels.at<int>((int)labelIdx));
}
// store the spatial histograms of the original data
for(size_t sampleIdx = 0; sampleIdx < src.size(); sampleIdx++) {
// calculate lbp image
Mat lbp_image = elbp(src[sampleIdx], _radius, _neighbors);
// get spatial histogram from this lbp image
Mat p = spatial_histogram(
lbp_image, /* lbp_image */
static_cast<int>(std::pow(2.0, static_cast<double>(_neighbors))), /* number of possible patterns */
_grid_x, /* grid size x */
_grid_y, /* grid size y */
true);
// add to templates
_histograms.push_back(p);
}
}训练进程分为以下几个进程:
- 首先进行必要的毛病检查,得到人脸图象向量和标签向量
- 计算lbp图象
- 根据lbp图象得到空间直方图
- 将空间直方图矩阵纳入到私有变量_histograms向量中
生成lbp空间直方图的进程:
* elbp函数用于生成lbp图象。
* spatial_histogram函数用于将lbp图象分块,对每个区块进行直方图统计。
LBPH的预测进程
下面给出了LBPH预测函数predict的源码,再进行分析。
void LBPH::predict(InputArray _src, int &minClass, double &minDist) const {
if(_histograms.empty()) {
// throw error if no data (or simply return ⑴?)
string error_message = "This LBPH model is not computed yet. Did you call the train method?";
CV_Error(CV_StsBadArg, error_message);
}
Mat src = _src.getMat();
// get the spatial histogram from input image
Mat lbp_image = elbp(src, _radius, _neighbors);
Mat query = spatial_histogram(
lbp_image, /* lbp_image */
static_cast<int>(std::pow(2.0, static_cast<double>(_neighbors))), /* number of possible patterns */
_grid_x, /* grid size x */
_grid_y, /* grid size y */
true /* normed histograms */);
// find 1-nearest neighbor
minDist = DBL_MAX;
minClass = -1;
for(int sampleIdx = 0; sampleIdx < _histograms.size(); sampleIdx++) {
double dist = compareHist(_histograms[sampleIdx], query, CV_COMP_CHISQR);
if((dist < minDist) && (dist < _threshold)) {
minDist = dist;
minClass = _labels.at<int>(sampleIdx);
}
}
}预测进程就比较简单了,首先将待查询点图象进行lbp编码并生成空间直方图,然后线性暴力的计算直方图的距离,终究输出距离最小的预测种别。
compareHist函数
通过cv::compareHist函数来评估两个直方图有多么不同、或多么类似,返回丈量距离。
类似度衡量的办法目前支持4种:
下一篇 Android从源码框架思路开始