Android的屏幕类型有几百种不同的尺寸,从小型的手机到大型的电视机。因此要使我们的利用程序兼容不同屏幕尺寸,才可让我们的利用提供给更多的用户使用。
1、支持不同的屏幕尺寸
1、使用“wrap_content"和”match_parent"
为了确保布局的灵活性,来适应不同尺寸的屏幕,我们应当使用“wrap_content"来匹配组件的最小尺寸和使用”match_parent"来设置某些视图来匹配父视图的大小。这样设置和直接设置视图大小(如48dip)不同的是该视图的空间可以随着屏幕尺寸(父视图的大小)随便扩大。例如以下布局:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "match_parent" >
<LinearLayout android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:id = "@+id/linearLayout1"
android:gravity = "center"
android:layout_height = "50dp" >
<ImageView android:id = "@+id/imageView1"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:src = "@drawable/logo"
android:paddingRight = "30dp"
android:layout_gravity = "left"
android:layout_weight = "0" />
<View android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:id = "@+id/view1"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_weight = "1" />
<Button android:id = "@+id/categorybutton"
android:background = "@drawable/button_bg"
android:layout_height = "match_parent"
android:layout_weight = "0"
android:layout_width = "120dp"
style = " @ style / CategoryButtonStyle " />
</LinearLayout>
<fragment android:id = "@+id/headlines"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.HeadlinesFragment"
android:layout_width = "match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
当我们翻转手机屏幕可以看到横向和竖向的屏幕适配以下:
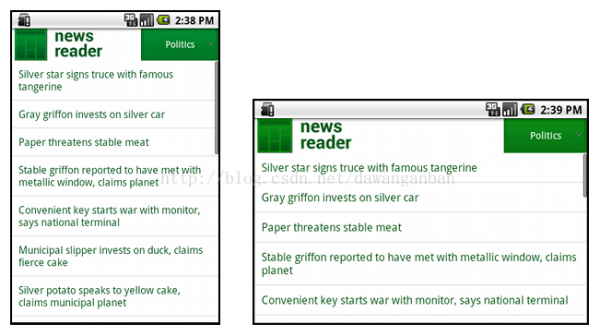
2、使用Relative_layout
我们可使用LinearLayout通过“wrap_content"和”match_parent"来实现很多复杂的布局,但是LinearLayout善于控制的是线性的关系,如果是要精确控制平面关系,使用Relative_layout比较适合,它可以指定两个组件之间的空间关系。例以下面代码:
<?xml的version = "1.0" encoding = "utf⑻" ?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "match_parent" >
<TextView
android:id = "@+id/label"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:text = "Type here:" />
<EditText
android:id = "@+id/entry"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_below = "@id/label" />
<Button
android:id = "@+id/ok"
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_below = "@id/entry"
android:layout_alignParentRight = "true"
android:layout_marginLeft = "10dp"
android:text = "OK" />
<Button
android:layout_width = "wrap_content"
android:layout_height = "wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf = "@id/ok"
android:layout_alignTop = "@id/ok"
android:text = "Cancel" />
</RelativeLayout>
在小屏幕尺寸的QVGA手机上显示以下:
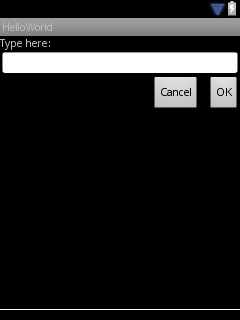
在大屏幕的WSVGA屏幕上显示以下:

3、使用尺寸限定符
上面我们通过“wrap_content"、”match_parent"、“relative_layout"的方法来实现不同屏幕尺寸的视图舒展,有效的解决了屏幕尺寸问题,除这些方法外我们还可使用尺寸限定符来针对不同的屏幕来做特殊的界面布局。
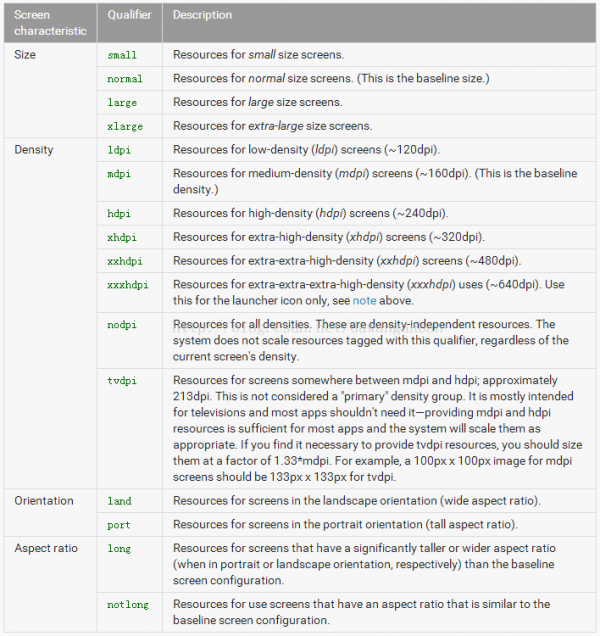
第1列是屏幕的特点,有尺寸、密度、方向、长宽比
第2列是限定符的写法(如large,我们就需要建立1个文件夹名称为layout-large)
第3列是相干解释和描写
例如我们现在在我们的res下建立两个文件夹通过不同的限定符文件夹名称来匹配不同尺寸的屏幕
res/layout/main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "match_parent" >
<fragment android:id = "@+id/headlines"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.HeadlinesFragment"
android:layout_width = "match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
res/layout-large/main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:orientation = "horizontal" >
<fragment android:id = "@+id/headlines"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.HeadlinesFragment"
android:layout_width = "400dp"
android:layout_marginRight = "10dp" />
<fragment android:id = "@+id/article"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.ArticleFragment"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
上面布局中在大屏幕中我们将两个大视图放到了全部屏幕,2小屏幕中我们只放置了1个视图。我们的装备会根据屏幕尺寸来自动寻觅自己的布局。
4、使用最小宽度限定符
上面根据屏幕尺寸来匹配不同的布局文件,但是很多时候我们可能在不同的大屏手机中需要分别显示不同的布局(例如Galaxy Tab显示5个还是7个),在Android3.2以后就有了最小宽度限定符来解决这个问题。
假定sw600dp来表示我们的最小宽度,则布局文件就能够有以下表示:
小屏幕手机适配的布局 res/layout/main.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation = "vertical"
android:layout_width = "match_parent"
android:layout_height = "match_parent" >
<fragment android:id = "@+id/headlines"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.HeadlinesFragment"
android:layout_width = "match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
装备宽度大于或等于600dp的布局 res/layout/layout-sw600dp.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:orientation = "horizontal" >
<fragment android:id = "@+id/headlines"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.HeadlinesFragment"
android:layout_width = "400dp"
android:layout_marginRight = "10dp" />
<fragment android:id = "@+id/article"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.ArticleFragment"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
要注意的是这类限定符在3.2之前的版本手机上是不支持的。在3.2之前还必须用尺寸限定符large来代替。
5、使用layout别名
综合上面的分析,如果我们要支持1个包括大屏幕尺寸的装备必须包括例以下面几个布局来匹配
res/layout/main.xml
res/layout/layout-large
res/layout/layout-sw600dp
最后这两个文件的作用是相同的,是为了支持3.2以下和以上版本,为了不混淆和保护难度,我们可以给这些布局起别名,比以下面的布局名:
res/layout/main.xml 单面板布局
res/layout/main_twopanes.xml 双面板布局
并添加这两个文件
res/values-large/layout.xml
<resources>
<item name="main" type="layout">@layout/main_twopanes</item>
</resources>
res/values-sw600dp/layout.xml
<resources>
<item name="main" type="layout">@layout/main_twopanes</item>
</resources>
可以看到这两个文件的内容相同,他们只是建立起1个main和mian_twospanes的联系,可以通过屏幕尺寸来分别获得不同的value文件下所对应的布局文件别名。
6、使用方向限定符
有的时候我们的利用可能需要翻转手性能取得更好的效果,此时的布局也需要做相应的改变,也能够分别做出对应的布局文件。请参照上面的表格(land 和 port)。
7、使用Nine-Patch图
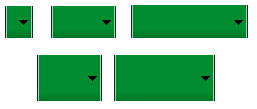
对不同的屏幕尺寸通常我们需要使用不同尺寸的图片资源,所以在设计可变大小的组件时,1定要使用Nine-Patch图。

如上图的Nine-Patch图在不同尺寸手机上的拉伸效果以下:
有关Nine-Patch的制作方法请参考我的另外一篇博文:http://blog.csdn.net/dawanganban/article/details/17379193
2、支持不同的屏幕密度
我们在设计布局的时候不能使用绝对的像素尺寸,而应当使用dp和sp.不同装备具有不同的屏幕密度,1英寸的不同密度手机上的像素个数是不同的。为了让大家弄清楚这些基本概念,我逐1解释1下:
dpi 像素密度:像素密度,即每英寸屏幕所具有的像素数,像素密度越大,显示画面细节就越丰富。
我们可以用这个公式表示 1dpi = 1pix / 1in
dp (dip)装备独立像素:在屏幕密度为160的显示屏上,1dip=1px
有了这些概念,我们来算1下,1dip是多长(是多少英寸)
result = in / dip
result = in / px (根据dp的定义)
result = 1 / (px / in)
result = 1 / dpi
result = 1 / 160
从上面的推导可以看出在屏幕密度为160的显示屏上 1dip其实就是 1 / 160 英寸,是1个屏幕尺寸上的绝对单位。
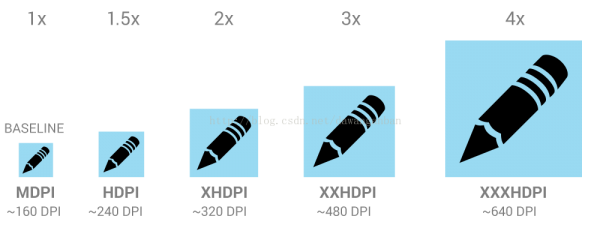
Android中为我们提供了适配不同分辨率的资源包,我们只需要做1套资源就能够自动帮我们换算成相应dpi(分辨率)下的尺寸,放大及缩小比例如上图所示。
3、不同UI的代码逻辑适配
1、肯定当前布局
public class NewsReaderActivity extends FragmentActivity {
boolean mIsDualPane ;
@Override
public void onCreate ( Bundle savedInstanceState ) {
super . onCreate ( savedInstanceState );
setContentView ( R . layout . main_layout );
View articleView = findViewById ( R . id . article );
mIsDualPane = articleView != null &&
articleView . getVisibility () == View . VISIBLE ;
}
}
如上面代码,我们可以通过某些View的可见性来判断选用的布局文件。
2、根据不同的布局,做出不同的逻辑
@Override
public void onHeadlineSelected(int index) {
mArtIndex = index;
if (mIsDualPane) {
/* display article on the right pane */
mArticleFragment.displayArticle(mCurrentCat.getArticle(index));
} else {
/* start a separate activity */
Intent intent = new Intent(this, ArticleActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("catIndex", mCatIndex);
intent.putExtra("artIndex", index);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
3、使用代码片断实现重用
<LinearLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:orientation = "horizontal" >
<fragment android:id = "@+id/headlines"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.HeadlinesFragment"
android:layout_width = "400dp"
android:layout_marginRight = "10dp" />
<fragment android:id = "@+id/article"
android:layout_height = "fill_parent"
android:name = "com.example.android.newsreader.ArticleFragment"
android:layout_width = "fill_parent" />
</LinearLayout>






