本文总结了图的深度优先搜索,图的广度优先搜索,邻接链表和邻接矩阵的实现,并查集的实现。
0),豫备知识
基础辞汇:有向图,无向图,带权有向图,带权无向图,有向图中<Vi, Vj>:即Vi--->Vj,弧尾--->弧头,无向图中相邻记为(Vi, Vj),顶点有穷集合V+边的有穷集合E。
图的两种实现方式:1,邻接矩阵:edge[n][n]表示有n个结点,数组内容为权值大小或是不是存在边(∞表示无边,权值或1表示有边,0表示结点到结点本身);
2,邻接链表:针对稀疏矩阵较适合,为图的每一个顶点都建立1个单链表,第i个单链表中保存与结点Vi所有相邻结点信息(无向图)或弧尾结点信息(有向图),和边信息。
1),图的深度优先搜索(DFS)
深度优先算法的主要思想是:首先以1个未被访问过的顶点作为起始顶点,沿当前顶点的边走到未访问过的顶点;当没有未访问过的顶点时,则回到上1个顶点,继续摸索访问别的顶点,直到所有的顶点都被访问过。明显,深度优先遍历是沿着图的某1条分支遍历直到末端,然后回溯,再沿着另外一条进行一样的遍历。
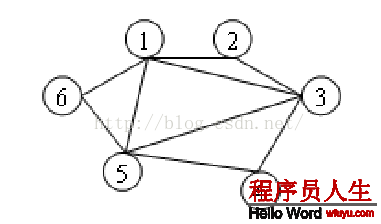
例1:以下图为例,从结点1开始DFS,程序的算法思想是:在主函数中初始化连接矩阵,调用dfs(1) ---> 设置变量cnt,将cnt等于结点个数作为dfs递归的临界条件 ---> 设置标志mark[n],铛铛前访问结点的边指向的下1结点未被访问时,进行dfs调度访问(结点的相邻结点的访问顺序为标号由小到大的顺序)
/***先输入n个结点,m条边,以后输入无向图的m条边,以后对上图输出DFS遍历的结点顺序***/
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#define nmax 110
#define inf 999999999
using namespace std;
int n, m, cnt, edge[nmax][nmax], mark[nmax];//结点数,边数,计数值,邻接矩阵,结点访问标记
void dfs(int cur){
cnt++;
/***operation***/
if(cnt == 1)
cout << cur;
else
cout << setw(3) << cur;
/***operation***/
if(cnt == n) return;
else{
int i;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(edge[cur][i] == 1 && mark[i] == 0){
mark[i] = 1;
dfs(i);
}
}
return;
}
}
int main(){
while(cin >> n >> m && n != 0){
//初始化邻接矩阵
int i, j;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++){
edge[i][j] = inf;
}
edge[i][i] = 0;
}
int a, b;
while(m--){
cin >> a >> b;
edge[a][b] = edge[b][a] = 1;
}
//以dnf(1)为出发点开始递归遍历
memset(mark, 0, sizeof(mark));
cnt = 0;
mark[1] = 1;
dfs(1);
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
程序运行结果:

例2:下面是城市的地图,注意是单向图,求城市1到城市5的最短距离
程序思路:从1号城市动身,可到达2号城市和5号城市,若依照1到n的顺序则先访问2号城市;访问完2号城市后,由于2号城市可到达的城市有3号和5号城市,我们访问3号城市;尔后,3号城市可到达1号,4号城市,由于1号城市已被访问过,我们访问4号城市;4号城市又可到达5号城市,我们最后访问5号城市。但是,1->2->3->4->5其实不1定是最短路径,我们需要撤除5号城市的访问标记,返回到4号城市,由于经过4号城市已访问过5号城市而又没有其他城市可访问;再返回到3号城市,经过3号城市访问过4号城市,则看看能否访问5号城市,不能则再返回到2号城市,这时候2号城市有路径直达5号城市,即1->2->5.....如此折回再前进,直至找到所有1号城市能到达5号城市的路径,取其中的最小值。
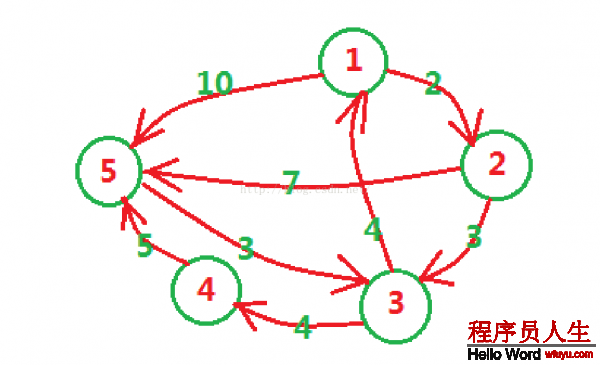
/***先输入n个结点,m条边,以后输入有向图的m条边,边的前两元素表示起始结点,第3个值表权值,输出1号城市到n号城市的最短距离***/
/***算法的思路是访问所有的深度遍历路径,需要在深度遍历返回时将访问标志置0***/
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#define nmax 110
#define inf 999999999
using namespace std;
int n, m, minPath, edge[nmax][nmax], mark[nmax];//结点数,边数,最小路径,邻接矩阵,结点访问标记
void dfs(int cur, int dst){
/***operation***/
/***operation***/
if(minPath < dst) return;//当前走过路径大于之前最短路径,没必要再走下去
if(cur == n){//临界条件
if(minPath > dst) minPath = dst;
return;
}
else{
int i;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(edge[cur][i] != inf && edge[cur][i] != 0 && mark[i] == 0){
mark[i] = 1;
dfs(i, dst+edge[cur][i]);
mark[i] = 0;
}
}
return;
}
}
int main(){
while(cin >> n >> m && n != 0){
//初始化邻接矩阵
int i, j;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++){
edge[i][j] = inf;
}
edge[i][i] = 0;
}
int a, b;
while(m--){
cin >> a >> b;
cin >> edge[a][b];
}
//以dnf(1)为出发点开始递归遍历
memset(mark, 0, sizeof(mark));
minPath = inf;
mark[1] = 1;
dfs(1, 0);
cout << minPath << endl;
}
return 0;
}
程序运行结果以下:
2),图的广度优先搜索(BFS)
广度优先遍历的主要思想是:首先以1个未被访问过的顶点作为起始顶点,访问其所有相邻的顶点,然后对每一个相邻的顶点,再访问它们相邻的未被访问过的顶点,直到所有顶点都被访问过,遍历结束。
例1:根据1)例1中的无向图,输出其广度优先搜索顺序。
程序主要思想:结点1入队 ---> while根据队列非空进行循环 ---> 出队并将相邻结点入队,另外需要设置计数值cnt,每次出队时加1。
/***先输入n个结点,m条边,以后输入无向图的m条边,边的两元素表示起始结点***/
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
#define nmax 110
#define inf 999999999
queue<int> que;
int n, m, mark[nmax], edge[nmax][nmax], cnt;
int main(){
while(cin >> n >> m && n != 0){
int i, j;
//初始化邻接链表
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++){
edge[i][j] = inf;
}
edge[i][i] = 0;
}
int a, b;
while(m--){
cin >> a >> b;
edge[a][b] = edge[b][a] = 1;
}
while(!que.empty()) que.pop();
memset(mark, 0, sizeof(mark));
//开始广度优先遍历
int head;
cnt = 0;
mark[1] = 1;
que.push(1);
while(!que.empty()){
head = que.front();
que.pop();
/***operation***/
cnt++;
if(cnt == 1)
cout << head;
else
cout << setw(3) << head;
/***operation***/
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(edge[head][i] == 1 && mark[i] == 0){
mark[i] = 1;
que.push(i);
}
}
}
cout << endl;
if(cnt != n) cout << "The original image is not connected.\n";
}
return 0;
}
程序运行结果以下:

例2:以下图,需要坐飞机从1号城市到5号城市,求最小的转机次数
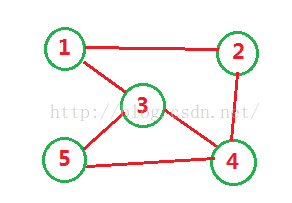
/***先输入n个结点,m条边,动身城市,终点城市,以后输入无向图的m条边,边的两元素表示起始结点***/
/***需要构建结点结构体Node,寄存结点编号和遍历层数,每次for循环时该层数在上1层基础上加1***/
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define nmax 110
#define inf 999999999
struct Node{
int node;
int cnt;
};
queue<Node> que;
int m, n, edge[nmax][nmax], mark[nmax], startNum, endNum;
int main(){
while(cin >> n >> m >> startNum >> endNum && n != 0){
bool tag = false;
//初始化邻接矩阵
int i, j;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(j = 1; j <= n; j++){
edge[i][j] = inf;
}
edge[i][i] = 0;
}
while(m--){
cin >> i >> j;
edge[i][j] = edge[j][i] = 1;
}
//开始广度优先遍历
memset(mark, 0, sizeof(mark));
while(!que.empty()) que.pop();
Node tmp;
tmp.node = startNum;
tmp.cnt = 0;
que.push(tmp);
mark[tmp.node] = 1;
while(!que.empty()){
Node head = que.front();
que.pop();
Node temp;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(edge[head.node][i] == 1 && mark[i] == 0){
temp.node = i;
temp.cnt = head.cnt + 1;
que.push(temp);//注意写在if语句里面
mark[temp.node] = 1;
if(temp.node == endNum){
tag = true;
cout << temp.cnt << endl;
break;
}
}
}
if(tag)
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
程序运行结果以下:

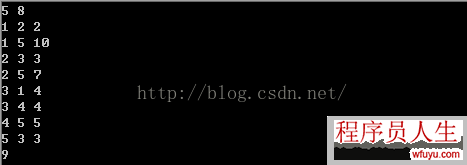
3),邻接链表和邻接矩阵的实现
邻接表由表头结点(结点信息)和表结点(边信息)两部份组成,其中图中每一个顶点均对应1个存储在数组中的表头结点。以下为带权有向图:
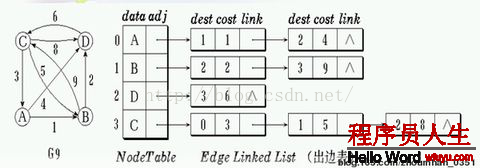
例1:邻接链表中每一个顶点均对应1个存储在数组中的表头结点,为简化,每一个邻接结点结构体只包括下1相邻结点编号和边权,使用标准模板vector编程实现。另外也可由邻接矩阵实现,上图实现以下:
/*****了解边信息结构体和邻接链表的实现,并在实现好基础上增加删除1些边,以后再用邻接矩阵实现,学习erase,push_back,setw的用法*****/
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <vector>
#define inf ⑴//设置无穷大为⑴,表示无边
using namespace std;
int n;
//边信息,包括连接结点编号和边的权重
struct Edge{
int adjNodeNum;
int edgeWeight;
};
struct Node{//结点信息
int nodeNum;
char data;
}node[110];
vector<Edge> adjList[110]; //邻接链表,该图最多有110个结点
int adjMatrix[110][110];//邻接矩阵
void initAdjList(){
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) adjList[i].clear();//清空--->构建--->具体操作
Edge tmp0[2], tmp1[2], tmp2, tmp3[3];
tmp0[0].adjNodeNum = 1; tmp0[0].edgeWeight = 1;
tmp0[1].adjNodeNum = 2; tmp0[1].edgeWeight = 4;
node[0].data = 'A'; node[0].nodeNum = 0;
adjList[0].push_back(tmp0[0]); adjList[0].push_back(tmp0[1]);
tmp1[0].adjNodeNum = 2; tmp1[0].edgeWeight = 2;
tmp1[1].adjNodeNum = 3; tmp1[1].edgeWeight = 9;
node[1].data = 'B'; node[1].nodeNum = 1;
adjList[1].push_back(tmp1[0]); adjList[1].push_back(tmp1[1]);
tmp2.adjNodeNum = 3; tmp2.edgeWeight = 6;
node[2].data = 'D'; node[2].nodeNum = 2;
adjList[2].push_back(tmp2);
tmp3[0].adjNodeNum = 0; tmp3[0].edgeWeight = 3;
tmp3[1].adjNodeNum = 1; tmp3[1].edgeWeight = 5;
tmp3[2].adjNodeNum = 2; tmp3[2].edgeWeight = 8;
adjList[3].push_back(tmp3[0]); adjList[3].push_back(tmp3[1]); adjList[3].push_back(tmp3[2]);
node[3].data = 'C'; node[3].nodeNum = 3;
}
void output(){
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
cout << node[i].nodeNum << setw(2) << node[i].data;
for(j = 0; j < adjList[i].size(); j++){
cout << setw(6) << adjList[i][j].adjNodeNum << setw(2) << adjList[i][j].edgeWeight;
}
cout << setw(9) << "NULL" << endl;
}
}
void makeChange(){
cout << "make some changes......:\n";
Edge temp;
temp.adjNodeNum = 3; temp.edgeWeight = 5;
adjList[0].push_back(temp);//邻接表0中增加1个元素
adjList[3].erase(adjList[3].begin()+1, adjList[3].begin()+3);//邻接表3中删除两个元素
}
void initMatrix(){
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(j = 0; j < n; j++){
adjMatrix[i][j] = inf;
}
adjMatrix[i][i] = 0;
}
adjMatrix[0][1] = 1; adjMatrix[0][2] = 4; adjMatrix[1][2] = 2;
adjMatrix[1][3] = 9; adjMatrix[2][3] = 6; adjMatrix[3][0] = 3;
adjMatrix[3][1] = 5; adjMatrix[3][2] = 8;
}
void output1(){
int i, j;
cout << "output the adjacency matrix:\n";
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
for(j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(j == 0) cout << adjMatrix[i][j];
else cout << setw(3) << adjMatrix[i][j];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main(){
n = 4;
initAdjList();
output();
makeChange();
output();
initMatrix();
output1();
return 0;
}
程序运行结果以下:
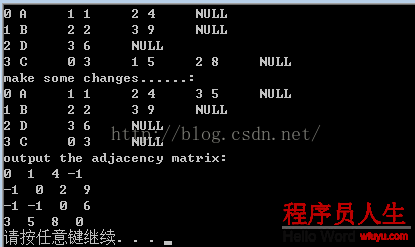
4),并查集的实现
并查集:用1棵树上的结点来表示在1个集合中的数字,如以下{1,2,3,4}和{5,6},再用每一个结点中的内容表示其双亲结点,如Tree[N],则Tree[1] = ⑴, Tree[2] = 1, Tree[6] = 5......
如果想要合并这两棵树棵树,则可令Tree[5] = ⑴变成Tree[5] = 1。以下:
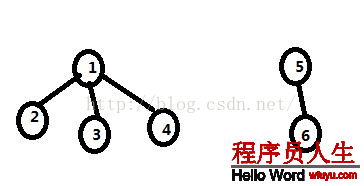
对,以下1种特殊情况,需要在查找树的根节点时,加以1定的束缚与优化,将遍历过的元素的双亲结点设为根节点,以下:
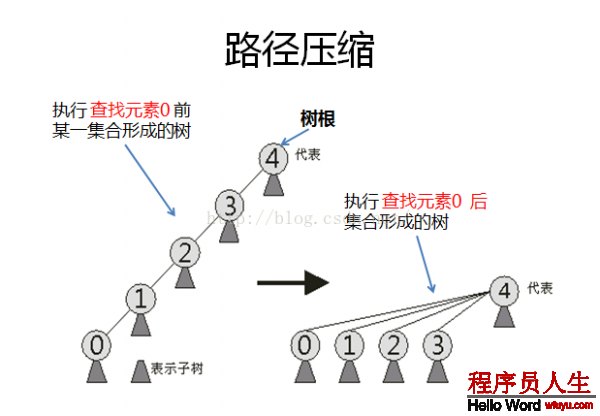
例1:并查集的实现
/****实现并查集的数组组成,找根节点,合并两个集合,紧缩路径************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int Set[110];
int Tree[110];
//使用查找函数来寻觅x所在树的根节点
int findRoot(int x){
if(Tree[x] == ⑴) return x;
else
return findRoot(Tree[x]);
}
//使用紧缩路径的查找函数来查找x所在树的根节点,只紧缩x到root所查找的路径
int findRoot1(int x){
if(Tree[x] == ⑴) return x;
else{
int tmp = findRoot1(Tree[x]);
Tree[x] = tmp;
return tmp;//层层返回
}
}
//使用非递归方式
int findRoot_(int x){
while(Tree[x] != ⑴) x = Tree[x];
return x;
}
int findRoot_1(int x){
int tmp = x;
while(Tree[x] != ⑴) x = Tree[x];
while(Tree[tmp] != ⑴) {tmp = Tree[tmp]; Tree[tmp] = x;}//tmp先保存父节点方便while循环,再对数组内容做改变
return x;
}
int main(){
int n1, n2;//集合1,2的元素个数
cout << "Please input the number of set1 and the number of set2:\n";
while(cin >> n1 >> n2){
int i = 0, j;
//输入集合1和2的数组表,第1行代表元素,第2行代表元素的双亲结点
cout << "Please input set1(first line is node, second line is its father node):\n";
for(i = 0; i < n1; i++) cin >> Set[i];
for(i = 0; i < n1; i++) cin >> Tree[Set[i]];
cout << "Please input set2(first line is node, second line is its father node):\n";
for(i = n1 ; i < n1 + n2; i++) cin >> Set[i];
for(i = n1 ; i < n1 + n2; i++) cin >> Tree[Set[i]];
//输入集合1和集合2中的1个元素,找出各自的根节点
cout << "Please input two nodes of the two sets (and output its root node):\n";
int sub1, sub2;
cin >> sub1 >> sub2;
cout << "It's root node is: " << findRoot(sub1) << " " << findRoot(sub2) << endl;
//合并集合1和集合2,并显示
cout << "Merge two trees:\n";
Tree[findRoot1(sub2)] = findRoot1(sub1);
for(i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++) cout << setw(2) <<Set[i];
cout << endl;
for(i = 0; i < n1 + n2; i++) cout << setw(2) << Tree[Set[i]];
cout << endl;
cout << "Please input the number of set1 and the number of set2:\n";
}
}
程序运行结果以下:
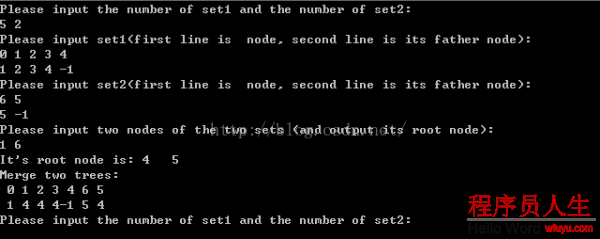
例2:畅通工程
/****输入城镇数n和道路数m,再输入每条道路连通的城镇(城镇从1开始编号),看最少需再修几条路使全部城镇连通;若输入n且n=0结束输入***********/
/****初始化n个并查集,尔后每输入1条道路,就将关联的两个城镇加入同1并查集,最后由独立的并查集个数⑴即为所求答案*********************/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Tree[1100];
int findRoot(int x){
if(Tree[x] == ⑴) return x;
else{
int tmp = findRoot(Tree[x]);
Tree[x] = tmp;
return tmp;
}
}
int main(){
int n, m;
while(cin >> n && n!= 0){
cin >> m;
int i;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)//初始化n个并查集
Tree[i] = ⑴;
int a, b;
for(i = m; i >= 1; i--){//处理m条道路,合并并查集
cin >> a >> b;
a = findRoot(a);
b = findRoot(b);
if(a != b) Tree[b] = a; //此处必须先进行比较,如果a,b相同,则会使根节点不为⑴,致使并查集总数变少
}
int count = 0;
for(i = 1; i <= n; i++)//计算剩余独立的并查集
if(Tree[i] == ⑴) ++count;
cout << "Need to build the number of roads is: " << count - 1 << endl;
}
}
程序运行结果以下:

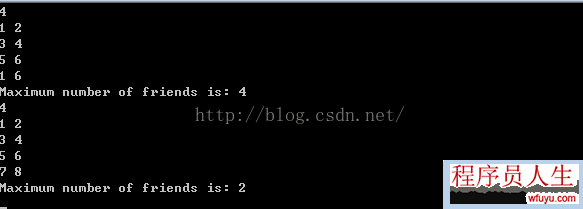
例3:More Is Better
/***有1000 0000个小朋友,随机选择朋友关系,每次选中两个人,且朋友关系具有传递性,当选择m次后,输出最大朋友关系人数或1**********************/
/***思路与畅通工程类似,初始化并查集,对每次选择进行并查集合并,由于需要计算最大并查集元素个数,需要初始化每一个sum[i]=1,每次合并都进行累加便可**/
/***先输入关系次数m,再顺次输入这m组关系****/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define num 10000001
int Tree[num];
int Sum[num];
int findRoot(int x){
if(Tree[x] == ⑴) return x;
else{
int tmp = findRoot(Tree[x]);
Tree[x] = tmp;
return tmp;
}
}
int main(){
int m;
while(cin >> m && m != 0){
int i;
for(i = 1; i < num; i++) {Tree[i] = ⑴; Sum[i] = 1;}
int a, b;
while(m--){
cin >> a >> b;
a = findRoot(a);
b = findRoot(b);
if(a != b) {Tree[b] = a; Sum[a] += Sum[b];}
}
int max = 1;
for(i = 1; i < num; i++)
if(Sum[i] > max) max = Sum[i];
cout << "Maximum number of friends is: " << max << endl;
}
return 0;
}
程序运行结果以下: