Spring 源码解析之DispatcherServlet源码解析(五)
Spring 源码解析之DispatcherServlet源码解析(5)
前言
本文需要有前4篇文章的基础,才能够清晰易懂,有兴趣可以先看看详细的流程,这篇文章可以说是第1篇文章,也能够说是前4篇文章的的汇总,Spring的全部要求流程都是围绕着
DispatcherServlet进行的
类结构图
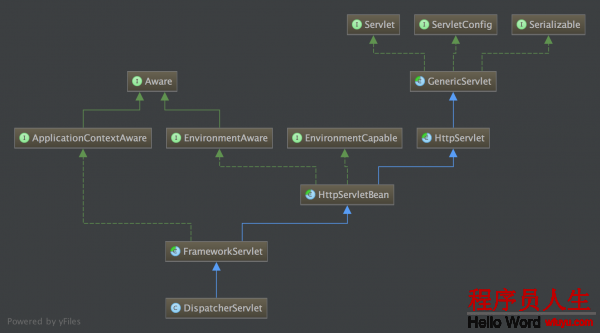
根据类的结构来讲DispatcherServlet本身也是继承了HttpServlet的,所有的要求都是根据这1个Servlet来进行转发的,同时解释了为何需要在web.xml进行以下配置,由于Spring是基于1个Servlet来展开的,固然不需要Servlet也能够使用Spring
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/spring-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping> 1 DispatcherServlet初始化
1.1 DispatcherServlet初始化加载的几个bean
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//初始化文件上传处理类
initMultipartResolver(context);
//初始化本地化Resolver
initLocaleResolver(context);
//初始化主题Resolver
initThemeResolver(context);
//初始化1些个与处理的HandlerMappings
initHandlerMappings(context);
//
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//初始化异常处理的handler
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//初始化要求路径转换为ViewName 的Translator
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//初始化ViewResolvers 这个就是针对视图处理的Resolvers 比如jsp处理Resolvers 或freemarker处理Resolvers
initViewResolvers(context);
//初始化 主要管理flashmap,比如RedirectAttributes 的属性会放到这个里面,默许使用的是SessionFlashMapManager
initFlashMapManager(context);
}1.2 初始化流程图
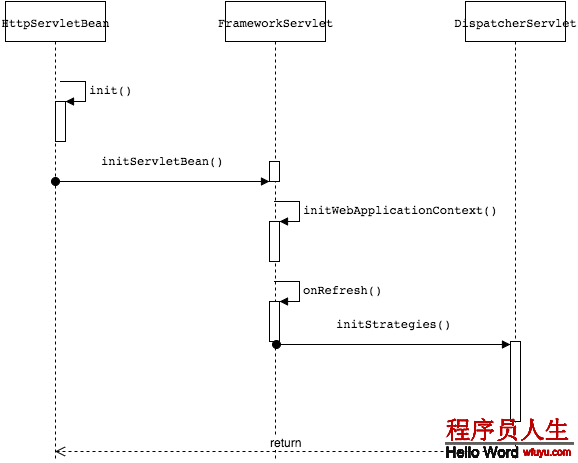
1.2.1 HttpServletBean源码解析
HttpServletBean本身来讲是1个普通的servlet而已,主要做1些资源的初始化
public abstract class HttpServletBean extends HttpServlet
implements EnvironmentCapable, EnvironmentAware {
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
/**
* Set of required properties (Strings) that must be supplied as
* config parameters to this servlet.
*/
private final Set<String> requiredProperties = new HashSet<String>();
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
/**
* Subclasses can invoke this method to specify that this property
* (which must match a JavaBean property they expose) is mandatory,
* and must be supplied as a config parameter. This should be called
* from the constructor of a subclass.
* <p>This method is only relevant in case of traditional initialization
* driven by a ServletConfig instance.
* @param property name of the required property
*/
protected final void addRequiredProperty(String property) {
this.requiredProperties.add(property);
}
/**
* Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and
* invoke subclass initialization.
* @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required
* properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails.
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
try {
//使用Servlet配置的初始化参数创建1个PropertyValues对象,PropertyValues对象是名值对的集合, 子类也能够指定哪些属性是必须的
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
//把当前的Servlet当作1个Bean, 把Bean的属性和属性的存取方法信息放入BeanWrapper对象
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
//注册1个可以在资源和路径之间进行转化的客户化编辑器,这些资源是这个Web利用的内部资源,例如,1个文件,1个图片等等
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
//提供给子类机会增加更多的客户化的编辑器,或对BeanWrapper进行更多的初始化
initBeanWrapper(bw);
//把初始化制定的参数值赋值到Servlet的属性中,第2个参数true表明疏忽位置属性
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
throw ex;
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
//提供给子类的的初始化方法 目前是FrameworkServlet 进行了实现
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
/**
* Initialize the BeanWrapper for this HttpServletBean,
* possibly with custom editors.
* <p>This default implementation is empty.
* @param bw the BeanWrapper to initialize
* @throws BeansException if thrown by BeanWrapper methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.BeanWrapper#registerCustomEditor
*/
protected void initBeanWrapper(BeanWrapper bw) throws BeansException {
}
/**
* Overridden method that simply returns {@code null} when no
* ServletConfig set yet.
* @see #getServletConfig()
*/
@Override
public final String getServletName() {
return (getServletConfig() != null ? getServletConfig().getServletName() : null);
}
/**
* Overridden method that simply returns {@code null} when no
* ServletConfig set yet.
* @see #getServletConfig()
*/
@Override
public final ServletContext getServletContext() {
return (getServletConfig() != null ? getServletConfig().getServletContext() : null);
}
/**
* Subclasses may override this to perform custom initialization.
* All bean properties of this servlet will have been set before this
* method is invoked.
* <p>This default implementation is empty.
* @throws ServletException if subclass initialization fails
*/
protected void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if environment is not assignable to
* {@code ConfigurableEnvironment}.
*/
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
* <p>If {@code null}, a new environment will be initialized via
* {@link #createEnvironment()}.
*/
@Override
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = this.createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}
/**
* Create and return a new {@link StandardServletEnvironment}. Subclasses may override
* in order to configure the environment or specialize the environment type returned.
*/
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
/**
* PropertyValues implementation created from ServletConfig init parameters.
*/
//主要是用来添加初始化参数的
private static class ServletConfigPropertyValues extends MutablePropertyValues {
/**
* Create new ServletConfigPropertyValues.
* @param config ServletConfig we'll use to take PropertyValues from
* @param requiredProperties set of property names we need, where
* we can't accept default values requiredProperties 这个参数主要是指定初始化时必须添加的参数
* @throws ServletException if any required properties are missing
*/
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
Set<String> missingProps = (requiredProperties != null && !requiredProperties.isEmpty()) ?
new HashSet<String>(requiredProperties) : null;
Enumeration<String> en = config.getInitParameterNames();
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
String property = en.nextElement();
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (missingProps != null && missingProps.size() > 0) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}
}
1.2.1 FrameworkServlet源码解析
这里只贴初始化的需要的部份代码,根据上面的逻辑,子类实现了initServletBean()这个方法进行初始化
public abstract class FrameworkServlet extends HttpServletBean implements ApplicationContextAware {
protected void initFrameworkServlet() throws ServletException {
}
//实现HttpServletBean 的初始化接口
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//初始化webApplicationContext
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//这个是留给子类去实现的方法,暂时来讲没有具体的实现,主要是留给开发人员自定义1些特性的时候
//这个时候WebApplicationContext已被初始化了,也就是1些个spring的配置文件已被初始化了
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//获得根的Context对象,比如说我用了Spring boot或注解的方式进行初始化,那末这里的Context就是Spring boot或其他的context对象
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
//如果当前的webApplicationContext 不等于null
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
//如果context对象是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
//如果ConfigurableWebApplicationContext 不是存活状态
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
//如果没有设置过parent
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
//查询当前的Context,下述有详细讲授
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
//如果没有找到那末就通过rootContext 去创建1个Context对象
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
//如果允许通过事件通知,那末就直接初始化。通过事件的通知可以反向的说明onRefresh()这个方法是可以被重复调用的,具体分析看下面
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
//如果允许publish Context的话那末就把spring context放入到spring的ServletContext中
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
//创建and refresh WebApplicationContext
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
//判断id
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + "/" + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
//添加针对ContextRefreshListener事件的监听
//ApplicationListener decorator that filters events from a specified event source, invoking its delegate listener for matching ApplicationEvent objects only.
//看了1下英文,大概是用了decorator(装潢)模式,具体源码里面,也只是做了1个简单的装潢模式,这个类接受所有的ApplicationEvent事件
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
//Post-process the given WebApplicationContext before it is refreshed
//大概就是说,在初始化handlermapping和1些本地化等调用refresh方法之前处理WebApplicationContext,这个类没有具体实现,开发者可以自己去处理
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
//spring dispatcherServlet初始化的时候可以指定初始化1些类
applyInitializers(wac);
//这个是重点方法,这里采取了事件的模式进行通知,去调用refresh方法初始化配置
wac.refresh();
}
//初始化spring context的时候 初始化1些指定需要初始化的类 这些类需要实现ApplicationContextInitializer 这个接口才能进行调用
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext wac) {
//获得到ServletContext中初始化的类数组参数
//
String globalClassNames = getServletContext().getInitParameter(ContextLoader.GLOBAL_INITIALIZER_CLASSES_PARAM);
if (globalClassNames != null) {
//不断的去初始化这个类数组 以,;\t\n等作为分隔符
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(globalClassNames, INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
this.contextInitializers.add(loadInitializer(className, wac));
}
}
if (this.contextInitializerClasses != null) {
for (String className : StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.contextInitializerClasses, INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS)) {
this.contextInitializers.add(loadInitializer(className, wac));
}
}
//排序,可以指定这些类的初始化顺序,通过@Order注解来实现排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.contextInitializers);
//初始化
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> initializer : this.contextInitializers) {
initializer.initialize(wac);
}
}
//初始化类,
private ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> loadInitializer(
String className, ConfigurableApplicationContext wac) {
try {
//加载这个类
Class<?> initializerClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, wac.getClassLoader());
//判断是不是实现了接口ApplicationContextInitializer
Class<?> initializerContextClass =
GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializerClass, ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
if (initializerContextClass != null && !initializerContextClass.isInstance(wac)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format(
"Could not apply context initializer [%s] since its generic parameter [%s] " +
"is not assignable from the type of application context used by this " +
"framework servlet: [%s]", initializerClass.getName(), initializerContextClass.getName(),
wac.getClass().getName()));
}
//初始化对象
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(initializerClass, ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(String.format("Could not load class [%s] specified " +
"via 'contextInitializerClasses' init-param", className), ex);
}
}
}
上述代码获得root Context的时候可以通过以下代码了解到获得方式,webapp的Context对象的保存,其实不过就是把spring的context放到了ServletContext的1个属性中而已
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());public abstract class WebApplicationContextUtils {
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
return getWebApplicationContext(sc, WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
/**
* Find a custom {@code WebApplicationContext} for this web app.
* @param sc ServletContext to find the web application context for
* @param attrName the name of the ServletContext attribute to look for
* @return the desired WebApplicationContext for this web app, or {@code null} if none
*/
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, String attrName) {
Assert.notNull(sc, "ServletContext must not be null");
//通过从ServletContext 去获得spring的context对象
Object attr = sc.getAttribute(attrName);
if (attr == null) {
return null;
}
if (attr instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) attr;
}
if (attr instanceof Exception) {
throw new IllegalStateException((Exception) attr);
}
if (!(attr instanceof WebApplicationContext)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Context attribute is not of type WebApplicationContext: " + attr);
}
return (WebApplicationContext) attr;
}
}wac = findWebApplicationContext(); 上述这块逻辑主要是通过获得ContextAttribute的属性名去ServletContext中获得Context对象
protected WebApplicationContext findWebApplicationContext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
WebApplicationContext wac =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext(), attrName);
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?");
}
return wac;
}1.2.2 FrameworkServlet 中refresh源码解析
这里流程比较繁琐,重点讲述1下 wac.refresh(); 这个方法会调用AbstractApplicationContext这里类面的refresh去实现相应的逻辑,这个类具体的英文解释(implements common context functionality. Uses the Template Method design pattern) 大概意思就是说实现了1些公有的方法,通过Template Method这类设计模式实现功能,其实也就是将逻辑放到了AbstractApplicationContext中,然后子类去实现各种方法。逻辑已由AbstractApplicationContext定好,子类不关心逻辑
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader
implements ConfigurableApplicationContext, DisposableBean {
//准备刷新之前调用
protected void prepareRefresh() {
//记录开始时间
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
//改变状态
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Refreshing " + this);
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment
//这个主要留给子类去实现
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
//校验必须初始化的参数
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<ApplicationEvent>();
}
//初始化1些beanFactory参数
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Tell the internal bean factory to use the context's class loader etc.
//设置classLoader
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
//设置bean表达式解析器 spring 的el 表达式
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//使用资源编辑器来填充指定的PropertyEditorRegistry。
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// Configure the bean factory with context callbacks.
//负责注入ResourceLoaderAware, ApplicationEventPublisherAware, MessageSourceAware, ApplicationContextAware ApplicationContext相干特性的Bean
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
// BeanFactory interface not registered as resolvable type in a plain factory.
// MessageSource registered (and found for autowiring) as a bean.
//This is intended for factory/context references that are supposed to be autowirable but are not defined as beans in the factory: e.g. a dependency of type ApplicationContext resolved to the ApplicationContext instance that the bean is living in.
//上述英文大概意思就是定义了1个特殊的bean,但是这个bean不通过 beanFactory进行管理生命周期,beanFactory本身就是1个bean,本身管理本身就有点奇怪,所以这个方法是注册1些特殊的bean,并且可以进行注入
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Register default environment beans.
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//preparecontext之前履行的操作
prepareRefresh();
//告知子类刷新bean工厂,spring boot能够做到改变1个类进行热部署,我猜可能就调用了这个刷新方法去刷新bean工厂,所以改变了1些静态变量spring boot是不会动态刷新的
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
//初始化1些bean工厂的参数
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 增加处理servletContext的类
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//初始化消息源
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
//初始化消息事件
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//发送refresh事件
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
}AbstractApplicationContext这个类比较繁琐,这里只大概描写了1下大概的功能,后续文章会详细进行讲授,这里主要是讲授初始化流程
Spring 整体流程图
