概述
Nginx 提供了两种全异步方式与第3方服务进行通讯:upstream 和subrequest。upstream
在与第3方服务器交互时(包括建立TCP 连接、发送要求、接收响应、关闭
TCP 连接),不会阻塞
Nginx 进程处理其他要求。subrequest 只是分解复杂要求的1种设计模式,它可以把原始要求分解为多个子要求,使得诸多要求协同完成1个用户要求,并且每一个要求只关注1个功能。subrequest 访问第3方服务终究也是基于
upstream 实现的。
upstream 被定义为访问上游服务器,它把Nginx 定义为反代理服务器,重要功能是透传,其次才是以
TCP 获得第3方服务器的内容。Nginx 的
HTTP 反向代理模块是基于
upstream 方式实现的。subrequest 是子要求,也就是说subrequest 将会为用户创建子要求,行将1个复杂的要求分解为多个子要求,每一个子要求负责1种功能项,而最初的原始要求负责构成并发送响应给用户。当subrequest
访问第3服务时,首先派生出子要求访问上游服务器,父要求在完全获得上游服务器的响应后再决定如何处理来自客户真个要求。
因此,若希望把是第3方服务的内容原封不动地返回给用户时,则使用
upstream 方式。若访问第3方服务是为了获得某些信息,再根据这些信息来构造响应并发给用户,则应使用
subrequest 方式。
upstream 使用方式
upstream 模块不产生自己的内容,而是通过要求后端服务器得到内容。Nginx 内部封装了要求并获得响应内容的全部进程,所以upstream 模块只需要开发若干回调函数,完成构造要求和解析响应等具体的工作。
ngx_http_request_t 结构体
首先了解 upstream 是如何嵌入到1个要求中,这里必须从要求结构体 ngx_http_request_t 入手,在该结构体中具有1个ngx_http_upstream_t 结构体类型的成员
upstream。要求结构体 ngx_http_request_t 定义在文件 src/http/ngx_http_request.h
中以下:
struct ngx_http_request_s {
uint32_t signature; /* "HTTP" */
/* 客户端连接 */
ngx_connection_t *connection;
/*
* 以下4个成员是保存模块对应的上下文结构指针;
* ctx 对应的是自定义的上下文结构指针;
* main_conf 对应的是main级别配置结构体的指针;
* srv_conf 对应的是server级别配置结构体的指针;
* loc_conf 对应的是location级别配置结构体的指针;
*/
void **ctx;
void **main_conf;
void **srv_conf;
void **loc_conf;
/*
* 以下两个是处理http要求;
* 当http头部接收终了,第1次在业务上处理http要求时,http框架提供的处理方法是ngx_http_process_request;
* 若该方法没法1次性处理完该要求的全部业务时,当控制权归还给epoll事件模块后,该要求再次被回调,
* 此时,将通过ngx_http_request_handler方法进行处理,而这个方法中对可读或可写事件的处理就是由函数
* read_event_handler或write_event_handler 来处理要求;
*/
ngx_http_event_handler_pt read_event_handler;
ngx_http_event_handler_pt write_event_handler;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
ngx_http_cache_t *cache;
#endif
/* 若使用upstream机制,则需要以下的结构体 */
ngx_http_upstream_t *upstream;
ngx_array_t *upstream_states;
/* of ngx_http_upstream_state_t */
/* 内存池 */
ngx_pool_t *pool;
/* 主要用于接收http要求头部内容的缓冲区 */
ngx_buf_t *header_in;
/*
* 调用函数ngx_http_request_headers 接收并解析http要求头部终了后,
* 则把解析完成的每个http头部加入到结构体headers_in的成员headers链表中,
* 同时初始化该结构体的其他成员;
*/
ngx_http_headers_in_t headers_in;
/*
* http模块将待发送的http相应的信息寄存在headers_out中,
* 并期望http框架将headers_out中的成员序列化为http响应包体发送个客户端;
*/
ngx_http_headers_out_t headers_out;
/* 接收要求包体的数据结构 */
ngx_http_request_body_t *request_body;
/* 延迟关闭连接的时间 */
time_t lingering_time;
/* 当前要求初始化的时间 */
time_t start_sec;
ngx_msec_t start_msec;
/*
* 以下的 9 个成员是函数ngx_http_process_request_line在接收、解析http要求行时解析出的信息 */
ngx_uint_t method; /* 方法名称 */
ngx_uint_t http_version; /* 协议版本 */
ngx_str_t request_line; /* 要求行 */
ngx_str_t uri; /* 客户要求中的uri */
ngx_str_t args; /* uri 中的参数 */
ngx_str_t exten; /* 客户要求的文件扩大名 */
ngx_str_t unparsed_uri; /* 没经过URI 解码的原始要求 */
ngx_str_t method_name; /* 方法名称字符串 */
ngx_str_t http_protocol;/* 其data成员指向要求中http的起始地址 */
/*
* 存储待发送给客户的http响应;
* out保存着由headers_out序列化后的表示http头部的TCP流;
* 调用ngx_http_output_filter方法后,out还保存这待发送的http包体;
*/
ngx_chain_t *out;
/*
* 当前要求多是用户要求,或是派生的子要求;
* main标识1序列相干的派生子要求的原始要求;
* 即通过main与当前要求的地址对照来判断是用户要求还是派生子要求;
*/
ngx_http_request_t *main;
/*
* 当前要求的父亲要求,但不1定是原始要求 */
ngx_http_request_t *parent;
/* 以下两个是与subrequest子要求相干的功能 */
ngx_http_postponed_request_t *postponed;
ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *post_subrequest;
/* 连接子要求的链表 */
ngx_http_posted_request_t *posted_requests;
/*
* 全局结构体ngx_http_phase_engine_t定义了1个ngx_http_phase_handler_t回调方法的数组;
* 而这里的phase_handler作为该数组的序列号表示指定数组中的回调方法,相当于数组的下标;
*/
ngx_int_t phase_handler;
/*
* 表示NGX_HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段提供给http模块要求的1种方式,它指向http模块实现的要求处理方法 */
ngx_http_handler_pt content_handler;
/*
* 在NGX――HTTP_CONTENT_PHASE阶段需要判断要求是不是具有访问权限时,
* 可通过
access_code来传递http模块的handler回调方法的返回值来判断,
* 若为0表示具有权限,否则不具有;
*/
ngx_uint_t
access_code;
ngx_http_variable_value_t *variables;
#if (NGX_PCRE)
ngx_uint_t ncaptures;
int *captures;
u_char *captures_data;
#endif
/* 限制当前要求的发送的速率 */
size_t limit_rate;
size_t limit_rate_after;
/* http响应的长度,不包括http响应头部 */
/* used to learn the Apache compatible response length without a header */
size_t header_size;
/* http要求的长度,包括http要求头部、http要求包体 */
off_t request_length;
/* 表示毛病状态标志 */
ngx_uint_t err_status;
/* http 连接 */
ngx_http_connection_t *http_connection;
#if (NGX_HTTP_SPDY)
ngx_http_spdy_stream_t *spdy_stream;
#endif
/* http日志处理函数 */
ngx_http_log_handler_pt log_handler;
/* 释放资源 */
ngx_http_cleanup_t *cleanup;
/* 以下都是1些标志位 */
/* 派生子要求 */
unsigned subrequests:8;
/* 作为原始要求的援用计数,每派生1个子要求,原始要求的成员count会增加1 */
unsigned count:8;
/* 阻塞标志位 */
unsigned blocked:8;
/* 标志位:为1表示当前要求是异步IO方式 */
unsigned aio:1;
unsigned http_state:4;
/* URI with "/." and on Win32 with "//" */
unsigned complex_uri:1;
/* URI with "%" */
unsigned quoted_uri:1;
/* URI with "+" */
unsigned plus_in_uri:1;
/* URI with " " */
unsigned space_in_uri:1;
unsigned invalid_header:1;
unsigned add_uri_to_alias:1;
unsigned valid_location:1;
unsigned valid_unparsed_uri:1;
/* 标志位:为1表示URI已被重写 */
unsigned uri_changed:1;
/* 表示URI被重写的次数 */
unsigned uri_changes:4;
unsigned request_body_in_single_buf:1;
unsigned request_body_in_file_only:1;
unsigned request_body_in_persistent_file:1;
unsigned request_body_in_clean_file:1;
unsigned request_body_file_group_
access:1;
unsigned request_body_file_log_level:3;
unsigned subrequest_in_memory:1;
unsigned waited:1;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
unsigned cached:1;
#endif
#if (NGX_HTTP_GZIP)
unsigned gzip_tested:1;
unsigned gzip_ok:1;
unsigned gzip_vary:1;
#endif
unsigned proxy:1;
unsigned bypass_cache:1;
unsigned no_cache:1;
/*
* instead of using the request context data in
* ngx_http_limit_conn_module and ngx_http_limit_req_module
* we use the single bits in the request structure
*/
unsigned limit_conn_set:1;
unsigned limit_req_set:1;
#if 0
unsigned cacheable:1;
#endif
unsigned pipeline:1;
unsigned chunked:1;
unsigned header_only:1;
unsigned keepalive:1;
unsigned lingering_close:1;
unsigned discard_body:1;
unsigned internal:1;
unsigned error_page:1;
unsigned ignore_content_encoding:1;
unsigned filter_finalize:1;
unsigned post_action:1;
unsigned request_complete:1;
unsigned request_output:1;
unsigned header_sent:1;
unsigned expect_tested:1;
unsigned root_tested:1;
unsigned done:1;
unsigned logged:1;
unsigned buffered:4;
unsigned main_filter_need_in_memory:1;
unsigned filter_need_in_memory:1;
unsigned filter_need_temporary:1;
unsigned allow_ranges:1;
unsigned single_range:1;
#if (NGX_STAT_STUB)
unsigned stat_reading:1;
unsigned stat_writing:1;
#endif
/* used to parse HTTP headers */
/* 当前的解析状态 */
ngx_uint_t state;
ngx_uint_t header_hash;
ngx_uint_t lowcase_index;
u_char lowcase_header[NGX_HTTP_LC_HEADER_LEN];
u_char *header_name_start;
u_char *header_name_end;
u_char *header_start;
u_char *header_end;
/*
* a memory that can be reused after parsing a request line
* via ngx_http_ephemeral_t
*/
u_char *uri_start;
u_char *uri_end;
u_char *uri_ext;
u_char *args_start;
u_char *request_start;
u_char *request_end;
u_char *method_end;
u_char *schema_start;
u_char *schema_end;
u_char *host_start;
u_char *host_end;
u_char *port_start;
u_char *port_end;
unsigned http_minor:16;
unsigned http_major:16;
};
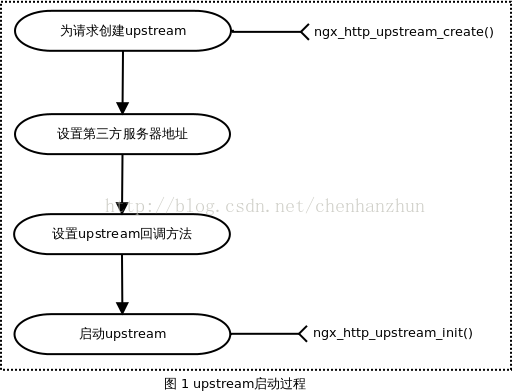
若没有实现 upstream 机制,则要求结构体 ngx_http_request_t 中的upstream成员设置为NULL,否则必须设置该成员。首先看下 HTTP 模块启动upstream
机制的进程:
- 调用函数 ngx_http_upstream_create 为要求创建upstream;
- 设置上游服务器的地址;可通过配置文件 nginx.conf 配置好上游服务器地址;也能够通过ngx_http_request_t 中的成员
resolved 设置上游服务器地址;
- 设置 upstream 的回调方法;
- 调用函数 ngx_http_upstream_init 启动upstream;
upstream 启动进程以下图所示:
ngx_http_upstream_t 结构体
upstream 结构体是
ngx_http_upstream_t,该结构体只在 upstream 模块内部使用,其定义在文件:src/http/ngx_http_upstream.h
/* ngx_http_upstream_t 结构体 */
struct ngx_http_upstream_s {
/* 处理读事件的回调方法,每个阶段都有不同的 read_event_handler */
ngx_http_upstream_handler_pt read_event_handler;
/* 处理写事件的回调方法,每个阶段都有不同的 write_event_handler */
ngx_http_upstream_handler_pt write_event_handler;
/* 表示主动向上游
服务器发起的连接 */
ngx_peer_connection_t peer;
/*
* 当向 下游客户端转发响应时(此时,ngx_http_request_t 结构体中的subrequest_in_memory标志位为0),
* 若已打开缓存且认为上游网速更快,此时会使用pipe成员来转发响应;
* 使用这类方式转发响应时,在HTTP模块使用upstream机制前必须构造pipe结构体;
*/
ngx_event_pipe_t *pipe;
/* 发送给上游
服务器的要求,在实现create_request方法时需设置它 */
ngx_chain_t *request_bufs;
/* 定义了向下游发送响应的方式 */
ngx_output_chain_ctx_t output;
ngx_chain_writer_ctx_t writer;
/* 指定upstream机制的运行方式 */
ngx_http_upstream_conf_t *conf;
/*
* HTTP模块实现process_header方法时,若希望upstream直接转发响应,
* 则需把解析出来的响应头部适配为HTTP的响应头部,同时需要把包头中的
* 信息设置到headers_in结构体中
*/
ngx_http_upstream_headers_in_t headers_in;
/* 解析主机域名,用于直接指定的上游
服务器地址 */
ngx_http_upstream_resolved_t *resolved;
/* 接收客户信息的缓冲区 */
ngx_buf_t from_client;
/*
* 接收上游
服务器响应包头的缓冲区,当不直接把响应转发给客户端,
* 或buffering标志位为0的情况转发包体时,接收包体的缓冲区依然使用buffer
*/
ngx_buf_t buffer;
off_t length;
/*
* out_bufs有两种不同意义:
* 1、当不需要转发包体,且默许使用input_filter方法处理包体时,
* out_bufs将会指向响应包体,out_bufs链表中产生多个ngx_but_t缓冲区,
* 每一个缓冲区都指向buffer缓存中的1部份,而这里只是调用recv方法接收到的1段TCP流;
* 2、当需要向下游转发包体时,这个链表指向上1次向下游转发响应到现在这段时间内接收自上游的缓存响应;
*/
ngx_chain_t *out_bufs;
/*
* 当需要向下游转发响应包体时,它表示上1次向下游转发响应时没有发送完的内容;
*/
ngx_chain_t *busy_bufs;
/*
* 这个链表用于回收out_bufs中已发送给下游的ngx_buf_t结构体;
*/
ngx_chain_t *free_bufs;
/*
* 处理包体前的初始化方法;
* 其中data参数用于传递用户数据结构,就是下面成员input_filter_ctx
*/
ngx_int_t (*input_filter_init)(void *data);
/*
* 处理包体的方法;
* 其中data参数用于传递用户数据结构,就是下面成员input_filter_ctx,
* bytes表示本次接收到包体的长度;
*/
ngx_int_t (*input_filter)(void *data, ssize_t bytes);
/* 用于传递HTTP自定义的数据结构 */
void *input_filter_ctx;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
ngx_int_t (*create_key)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
#endif
/* HTTP模块实现的create_request方法用于构造发往上游
服务器的要求 */
ngx_int_t (*create_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/* 与上游
服务器的通讯失败后,若想再次向上游
服务器发起连接,则调用该函数 */
ngx_int_t (*reinit_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/*
* 解析上游
服务器返回的响应包头,该函数返回4个值中的1个:
* NGX_AGAIN 表示包头没有接收完全;
* NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_INVALID_HEADER 表示包头不合法;
* NGX_ERROR 表示出现毛病;
* NGX_OK 表示解析到完全的包头;
*/
ngx_int_t (*process_header)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/* 当客户端放弃要求时被调用,由于系统会自动关闭连接,因此,该函数不会进行任何具体操作 */
void (*abort_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/* 结束upstream要求时会调用该函数 */
void (*finalize_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_int_t rc);
/*
* 在上游返回的响应出现location或refresh头部表示重定向时,
* 会通过ngx_http_upstream_process_headers方法调用到可由HTTP模块
* 实现的rewrite_redirect方法;
*/
ngx_int_t (*rewrite_redirect)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_table_elt_t *h, size_t prefix);
ngx_int_t (*rewrite_cookie)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_table_elt_t *h);
ngx_msec_t timeout;
/* 用于表示上游响应的状态:毛病编码、包体长度等信息 */
ngx_http_upstream_state_t *state;
ngx_str_t method;
ngx_str_t schema;
ngx_str_t uri;
ngx_http_cleanup_pt *cleanup;
/* 以下是1些标志位 */
unsigned store:1;
unsigned cacheable:1;
unsigned accel:1;
unsigned ssl:1;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
unsigned cache_status:3;
#endif
unsigned buffering:1;
unsigned keepalive:1;
unsigned upgrade:1;
unsigned request_sent:1;
unsigned header_sent:1;
};
下面看下 upstream 处理上游响应包体的3种方式:
- 当要求结构体 ngx_http_request_t 中的成员subrequest_in_memory 标志位为 1 时,upstream 不转发响应包体到下游,并由HTTP
模块实现的 input_filter() 方法处理包体;
- 当要求结构体 ngx_http_request_t 中的成员subrequest_in_memory 标志位为 0 时,且
ngx_http_upstream_conf_t 配置结构体中的成员
buffering 标志位为 1 时,upstream 将开启更多的内存和磁盘文件用于缓存上游的响应包体(此时,上游网速更快),并转发响应包体;
- 当要求结构体 ngx_http_request_t 中的成员subrequest_in_memory 标志位为 0 时,且
ngx_http_upstream_conf_t 配置结构体中的成员
buffering 标志位为 0 时,upstream 将使用固定大小的缓冲区来转发响应包体;
ngx_http_upstream_conf_t 结构体
在结构体 ngx_http_upstream_t 的成员conf 中,conf 是1个结构体ngx_http_upstream_conf_t
变量,该变量设置了upstream 的限制性参数。ngx_http_upstream_conf_t 结构体定义以下:src/http/ngx_http_upstream.h
/* ngx_http_upstream_conf_t 结构体 */
typedef struct {
/*
* 若在ngx_http_upstream_t结构体中没有实现resolved成员时,
* upstream这个结构体才会生效,定义上游
服务器的配置;
*/
ngx_http_upstream_srv_conf_t *upstream;
/* 建立TCP连接的超时时间 */
ngx_msec_t connect_timeout;
/* 发送要求的超时时间 */
ngx_msec_t send_timeout;
/* 接收响应的超时时间 */
ngx_msec_t read_timeout;
ngx_msec_t timeout;
/* TCP的SO_SNOLOWAT选项,表示发送缓冲区的下限 */
size_t send_lowat;
/* ngx_http_upstream_t中的buffer大小 */
size_t buffer_size;
size_t busy_buffers_size;
/* 临时文件的最大长度 */
size_t max_temp_file_size;
/* 表示缓冲区中的响应写入到临时文件时1次写入字符流的最大长度 */
size_t temp_file_write_size;
size_t busy_buffers_size_conf;
size_t max_temp_file_size_conf;
size_t temp_file_write_size_conf;
/* 以缓存响应的方式转发上游
服务器的包体时所使用的内存大小 */
ngx_bufs_t bufs;
/* ignore_headers使得upstream在转发包头时跳过对某些头部的处理 */
ngx_uint_t ignore_headers;
/*
* 以2进制位来处理毛病码,若处理上游响应时发现这些毛病码,
* 那末在未将响应转发给下游客户端时,将会选择1个上游
服务器来重发要求;
*/
ngx_uint_t next_upstream;
/* 表示所创建的目录与文件的权限 */
ngx_uint_t store_
access;
/* 转发响应方式的标志位 */
ngx_flag_t buffering;
ngx_flag_t pass_request_headers;
ngx_flag_t pass_request_body;
ngx_flag_t ignore_client_abort;
ngx_flag_t intercept_errors;
ngx_flag_t cyclic_temp_file;
/* 寄存临时文件的目录 */
ngx_path_t *temp_path;
/* 不转发的头部 */
ngx_hash_t hide_headers_hash;
/*
* 当转发上游响应头部到下游客户端时,
* 若不希望将某些头部转发,则设置在这个数组中
*/
ngx_array_t *hide_headers;
/*
* 当转发上游响应头部到下游客户端时,
* 若希望将某些头部转发,则设置在这个数组中
*/
ngx_array_t *pass_headers;
/* 连接上游
服务器的本机地址 */
ngx_http_upstream_local_t *local;
#if (NGX_HTTP_CACHE)
ngx_shm_zone_t *cache;
ngx_uint_t cache_min_uses;
ngx_uint_t cache_use_stale;
ngx_uint_t cache_methods;
ngx_flag_t cache_lock;
ngx_msec_t cache_lock_timeout;
ngx_flag_t cache_revalidate;
ngx_array_t *cache_valid;
ngx_array_t *cache_bypass;
ngx_array_t *no_cache;
#endif
/*
* 当ngx_http_upstream_t 中的store标志位为1时,
* 如果需要将上游的响应寄存在文件中,
* store_lengths表示寄存路径的长度;
* store_values表示寄存路径;
*/
ngx_array_t *store_lengths;
ngx_array_t *store_values;
signed store:2;
unsigned intercept_404:1;
unsigned change_buffering:1;
#if (NGX_HTTP_SSL)
ngx_ssl_t *ssl;
ngx_flag_t ssl_session_reuse;
#endif
/* 使用upstream的模块名称,仅用于记录日志 */
ngx_str_t module;
} ngx_http_upstream_conf_t;
在 HTTP 反向代理模块在配置文件
nginx.conf 提供的配置项大都是用来设置结构体 ngx_http_upstream_conf_t 的成员。3 个超时时间成员是必须要设置的,由于他们默许是 0,即若不设置这 3 个成员,则没法与上游服务器建立TCP 连接。每个要求都有独立的
ngx_http_upstream_conf_t 结构体,因此,每一个要求都可以具有不同的网络超时时间等配置。
例如,将 nginx.conf 文件中的
upstream_conn_timeout 配置项解析到 ngx_http_hello_conf_t 结构体中的成员upstream.conn_timeout 中。可定义以下的连接超时时间,并把ngx_http_hello_conf_t
配置项的 upstream 成员赋给
ngx_http_upstream_t 中的conf 便可;
typedef struct
{
...
ngx_http_upstream_conf_t upstream;
}ngx_http_hello_conf_t;
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_hello_commands[] = {
{
ngx_string("upstream_conn_timeout"),
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF|NGX_CONF_TAKE1,
ngx_conf_set_msec_slot,
NGX_HTTP_LOC_CONF_OFFSET,
offsetof(ngx_http_hello_conf_t, upstream.conn_timeout),
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
/* 在 ngx_http_hello_handler 方法中以下定义 */
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_hello_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
...
ngx_http_hello_conf_t *mycf = (ngx_http_hello_conf_t *)ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r,ngx_http_hello_module);
r->upstream->conf = &mycf->upstream;
...
}
设置第3方服务器地址
在 ngx_http_upstream_t 结构体中的resolved 成员可直接设置上游服务器的地址,也能够由
nginx.conf 文件中配置
upstream 模块,并指定上游服务器的地址。resolved 类型定义以下:
typedef struct {
/* 主机名称 */
ngx_str_t host;
/* 端口号 */
in_port_t port;
ngx_uint_t no_port; /* unsigned no_port:1 */
/* 地址个数 */
ngx_uint_t naddrs;
/* 地址 */
ngx_addr_t *addrs;
/* 上游
服务器地址 */
struct sockaddr *sockaddr;
/* 上游
服务器地址长度 */
socklen_t socklen;
ngx_resolver_ctx_t *ctx;
} ngx_http_upstream_resolved_t;
设置回调方法
在结构体 ngx_http_upstream_t 中定义了 8 个回调方法:
/*
* 处理包体前的初始化方法;
* 其中data参数用于传递用户数据结构,就是下面成员input_filter_ctx
*/
ngx_int_t (*input_filter_init)(void *data);
/*
* 处理包体的方法;
* 其中data参数用于传递用户数据结构,就是下面成员input_filter_ctx,
* bytes表示本次接收到包体的长度;
*/
ngx_int_t (*input_filter)(void *data, ssize_t bytes);
/* 用于传递HTTP自定义的数据结构 */
void *input_filter_ctx;
/* HTTP模块实现的create_request方法用于构造发往上游
服务器的要求 */
ngx_int_t (*create_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/* 与上游
服务器的通讯失败后,若想再次向上游
服务器发起连接,则调用该函数 */
ngx_int_t (*reinit_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/*
* 解析上游
服务器返回的响应包头,该函数返回4个值中的1个:
* NGX_AGAIN 表示包头没有接收完全;
* NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_INVALID_HEADER 表示包头不合法;
* NGX_ERROR 表示出现毛病;
* NGX_OK 表示解析到完全的包头;
*/
ngx_int_t (*process_header)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/* 当客户端放弃要求时被调用,由于系统会自动关闭连接,因此,该函数不会进行任何具体操作 */
void (*abort_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/* 结束upstream要求时会调用该函数 */
void (*finalize_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_int_t rc);
/*
* 在上游返回的响应出现location或refresh头部表示重定向时,
* 会通过ngx_http_upstream_process_headers方法调用到可由HTTP模块
* 实现的rewrite_redirect方法;
*/
ngx_int_t (*rewrite_redirect)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_table_elt_t *h, size_t prefix);
在这些回调方法中,其中有 3 个非常重要,在模块中是必须要实现的,这 3 个回调函数为:
/* HTTP模块实现的create_request方法用于构造发往上游
服务器的要求 */
ngx_int_t (*create_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/*
* 解析上游
服务器返回的响应包头,该函数返回4个值中的1个:
* NGX_AGAIN 表示包头没有接收完全;
* NGX_HTTP_UPSTREAM_INVALID_HEADER 表示包头不合法;
* NGX_ERROR 表示出现毛病;
* NGX_OK 表示解析到完全的包头;
*/
ngx_int_t (*process_header)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
/* 结束upstream要求时会调用该函数 */
void (*finalize_request)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_int_t rc);
create_request 在初始化
upstream 时被调用,生成发送到后端服务器的要求缓冲(缓冲链)。reinit_request 在某台后端服务器出错的情况,Nginx 会尝试连接到另外一台后端服务器。Nginx 选定新的服务器以后,会先调用此函数,以重新初始化upstream
模块的工作状态,然后再次进行 upstream 连接。process_request 是用于解析上游服务器返回的基于TCP 的响应头部。finalize_request
在正常完成与后端服务器的要求后 或 失败 致使烧毁要求时,该方法被调用。input_filter_init 和input_filter 都用于处理上游的响应包体,由于在处理包体前HTTP 模块可能需要做1些初始化工作。初始化工作由
input_filter_init 完成,实际处理包体由
input_filter 方法完成。
启动 upstream 机制
调用 ngx_http_upstream_init 方法即可启动upstream 机制,此时,必须通过返回
NGX_DONE 通知
HTTP 框架暂停履行要求的下1个阶段,并且需要履行r->main->count++ 告知
HTTP 框架将当前要求的援用计数增加 1,即告知
ngx_http_hello_handler 方法暂时不要烧毁要求,由于HTTP 框架只有在援用计数为 0 时才真正烧毁要求。例如:
static ngx_int_t ngx_http_hello_handler(ngx_http_request_t *r)
{
...
r->main->count++;
ngx_http_upstream_init(r);
return NGX_DONE;
}
subrequest 使用方式
subrequest 只是分解复杂要求的1种设计模式,它可以把原始要求分解为多个子要求,使得诸多要求协同完成1个用户要求,并且每一个要求只关注1个功能。首先,若不是完全将上游服务器的响应包体转发到下游客户端,基本都会使用subrequest 创建子要求,并由子要求使用
upstream 机制访问上游服务器,然后由父要求根据上游响应重新构造返回给下游客户真个响应。
subrequest 的使用步骤以下:
- 在 nginx.conf 配置文件中配置好子要求的处理方式;
- 启动 subrequest 子要求;
- 实现子要求履行结束时的回调函数;
- 实现父要求被激活时的回调函数;
配置子要求的处理方式
子要求其实不是由 HTTP 框架解析所接收到客户端网络包而得到的,而是由父要求派生的。它的配置和普通要求的配置相同,都是在nginx.conf 文件中配置相应的处理模块。例如:可以在配置文件nginx.conf
中配置以下的子要求访问 https://github.com
location /subrq {
rewrite ^/subrq(.*)$ $1 break;
proxy_pass https://github.com;
}
启动 subrequest 子要求
subrequest 是在父要求的基础上派生的子要求,subrequest 返回的内容会被附加到父要求上面,他的实现方法是调用ngx_http_subrequest 函数,该函数定义在文件:src/http/ngx_http_core_module.h
ngx_int_t ngx_http_subrequest(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_str_t *uri, ngx_str_t *args, ngx_http_request_t **psr,
ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *ps, ngx_uint_t flags);
该函数的参数以下:援用自文件《Emiller's Advanced Topics In Nginx Module Development》
- *r is the original request(当前的要求,即父要求);
- *uri and*args
refer to the sub-request(*uri 是子要求的URI,*args是子要求
URI 的参数);
- **psr is a reference to a NULL pointer that will point to the new (sub-)request structure(**psr
是指向返回子要求,相当于值-结果传递,作为参数传递进去是指向 NULL 指针,输出结果是指向新创建的子要求);
- *ps is a callback for when the subrequest is finished. (*ps
是指出子要求结束时必须回调的处理方法);
- flags can be a bitwise-OR'ed combination of:
- NGX_HTTP_ZERO_IN_URI: the URI contains a character with ASCII code 0 (also known as '�'), or contains "%00"
- NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_IN_MEMORY: store the result of the subrequest in a contiguous chunk of memory (usually not necessary) (将子要求的subrequest_in_memory
标志位为 1,表示发起的子要求,访问的网络资源返回的响应将全部在内存中处理);
- NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_WAITED: store the result of the subrequest in a contiguous chunk of memory (usually not necessary) (将子要求的waited
标志位为 1,表示子要求完成后会设置本身的r->done 标志位,可以通过判断该标志位得知子要求是不是完成);
该函数 ngx_http_subrequest 的返回值以下:
- NGX_OK:the subrequest finished without touching the network(成功建立子要求);
- NGX_DONE:the client reset the network connection(客户端重置网络连接);
- NGX_ERROR:there was a server error of some sort(建立子要求失败);
- NGX_AGAIN:the subrequest requires network activity(子要求需要激活网络);
该子要求返回的结果附加在你期望的位置。若要修改子要求的结果,可使用
another filter(或同1个)。并告知该 filter 对父要求或子要求进行操作:具体实例可参照模块"addition"
module
if (r == r->main) {
/* primary request */
} else {
/* subrequest */
}
以下是子要求函数 ngx_http_subrequest 的源码剖析,其源码定义在文件:src/http/ngx_http_core_module.c
/* ngx_http_subrequest 函数 */
ngx_int_t
ngx_http_subrequest(ngx_http_request_t *r,
ngx_str_t *uri, ngx_str_t *args, ngx_http_request_t **psr,
ngx_http_post_subrequest_t *ps, ngx_uint_t flags)
{
ngx_time_t *tp;
ngx_connection_t *c;
ngx_http_request_t *sr;
ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf;
ngx_http_postponed_request_t *pr, *p;
/* 原始要求的子要求减少1个 */
r->main->subrequests--;
/* 若没有子要求则出错返回 */
if (r->main->subrequests == 0) {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ERR, r->connection->log, 0,
"subrequests cycle while processing "%V"", uri);
r->main->subrequests = 1;
return NGX_ERROR;
}
/* 分配内存sr */
sr = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_request_t));
if (sr == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
/* 设置为 HTTP 模块 */
sr->signature = NGX_HTTP_MODULE;
/* 设置sr的客户端连接 */
c = r->connection;
sr->connection = c;
/* 为自定义上下文结构分配内存 */
sr->ctx = ngx_pcalloc(r->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
if (sr->ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
/* 初始化headers链表,该链表存储待发送的http响应包体 */
if (ngx_list_init(&sr->headers_out.headers, r->pool, 20,
sizeof(ngx_table_elt_t))
!= NGX_OK)
{
return NGX_ERROR;
}
/* 设置main、server、location级别的配置结构体指针 */
cscf = ngx_http_get_module_srv_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
sr->main_conf = cscf->ctx->main_conf;
sr->srv_conf = cscf->ctx->srv_conf;
sr->loc_conf = cscf->ctx->loc_conf;
/* 设置内存池 */
sr->pool = r->pool;
/* 设置headers_in成员,该成员保存解析完成的http头部 */
sr->headers_in = r->headers_in;
ngx_http_clear_content_length(sr);
ngx_http_clear_accept_ranges(sr);
ngx_http_clear_last_modified(sr);
/* 设置接收要求包体的数据结构 */
sr->request_body = r->request_body;
#if (NGX_HTTP_SPDY)
sr->spdy_stream = r->spdy_stream;
#endif
/* 要求的方法名称 */
sr->method = NGX_HTTP_GET;
/* 要求协议的版本 */
sr->http_version = r->http_version;
/* 要求行 */
sr->request_line = r->request_line;
/* 要求中的uri */
sr->uri = *uri;
/* uri中的参数 */
if (args) {
sr->args = *args;
}
ngx_log_debug2(NGX_LOG_DEBUG_HTTP, c->log, 0,
"http subrequest "%V?%V"", uri, &sr->args);
/* 标志位 */
sr->subrequest_in_memory = (flags & NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_IN_MEMORY) != 0;
sr->waited = (flags & NGX_HTTP_SUBREQUEST_WAITED) != 0;
sr->unparsed_uri = r->unparsed_uri;
sr->method_name = ngx_http_core_get_method;
sr->http_protocol = r->http_protocol;
ngx_http_set_exten(sr);
/* 原始要求 */
sr->main = r->main;
sr->parent = r;/* 当前要求,即新创建子要求的父要求 */
sr->post_subrequest = ps;/* 子要求履行结束时,履行的回调方法 */
/* http要求的可读或可写事件的处理方法 */
sr->read_event_handler = ngx_http_request_empty_handler;
sr->write_event_handler = ngx_http_handler;
/* 保存当前可以向out chain输出数组的要求 */
if (c->data == r && r->postponed == NULL) {
c->data = sr;
}
/* 默许同享父要求的变量,也能够根据需求创建完子要求后,再创建子要求独立的变量集 */
sr->variables = r->variables;
/* 日志处理方法 */
sr->log_handler = r->log_handler;
pr = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_postponed_request_t));
if (pr == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
pr->request = sr;
pr->out = NULL;
pr->next = NULL;
/* 把该子要求挂载到其父要求的postponed链表队尾 */
if (r->postponed) {
for (p = r->postponed; p->next; p = p->next) { /* void */ }
p->next = pr;
} else {
r->postponed = pr;
}
/* 子要求为内部要求 */
sr->internal = 1;
/* 继承父要求的部份状态 */
sr->discard_body = r->discard_body;
sr->expect_tested = 1;
sr->main_filter_need_in_memory = r->main_filter_need_in_memory;
sr->uri_changes = NGX_HTTP_MAX_URI_CHANGES + 1;
tp = ngx_timeofday();
sr->start_sec = tp->sec;
sr->start_msec = tp->msec;
/* 增加原始要求的援用计数 */
r->main->count++;
*psr = sr;/* 指向新创建的子要求 */
/* 将该子要求挂载到原始要求的posted_requests链表队尾 */
return ngx_http_post_request(sr, NULL);
}
/* 其中 ngx_http_post_request 定义在文件 src/http/ngx_http_request.c */
ngx_int_t
ngx_http_post_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_http_posted_request_t *pr)
{
ngx_http_posted_request_t **p;
if (pr == NULL) {
pr = ngx_palloc(r->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_posted_request_t));
if (pr == NULL) {
return NGX_ERROR;
}
}
pr->request = r;
pr->next = NULL;
for (p = &r->main->posted_requests; *p; p = &(*p)->next) { /* void */ }
*p = pr;
return NGX_OK;
}
子要求结束时的回调函数
在子要求结束时(正常或异常结束)Nginx 会调用ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt 回调解理方法。下面是回调方法的定义:
typedef struct {
ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt handler;
void *data;
} ngx_http_post_subrequest_t;
typedef ngx_int_t (*ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt)(ngx_http_request_t *r,
void *data, ngx_int_t rc);
在结构体 ngx_http_post_subrequest_t 中,生成该结构体的变量时,可把用户的任意数据赋给指针data ,ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt 回调方法的参数data
就是用户把数据赋给结构体 ngx_http_post_subrequest_t 中的成员指针
data 所指的数据。ngx_http_post_subrequest_pt 回调方法中的参数rc 是子要求结束时的状态,它的取值由函数
ngx_http_finalize_request 烧毁要求时传递给参数
rc。 函数
ngx_http_finalize_request 的部份源码,具体可查阅文件:src/http/ngx_http_request.c
void
ngx_http_finalize_request(ngx_http_request_t *r, ngx_int_t rc)
{
...
/* 如果当前要求是某个原始要求的1个子要求,检查它是不是有回调handler处理函数,若存在则履行 */
if (r != r->main && r->post_subrequest) {
rc = r->post_subrequest->handler(r, r->post_subrequest->data, rc);
}
...
/* 若 r 是子要求 */
if (r != r->main) {
/* 该子要求还有未处理完的数据或子要求 */
if (r->buffered || r->postponed) {
/* 添加1个该子要求的写事件,并设置适合的write event hander,
以便下次写事件来的时候继续处理,这里实际上下次履行时会调用ngx_http_output_filter函数,
终究还是会进入ngx_http_postpone_filter进行处理 */
if (ngx_http_set_write_handler(r) != NGX_OK) {
ngx_http_terminate_request(r, 0);
}
return;
}
...
pr = r->parent;
/* 该子要求已处理终了,如果它具有发送数据的权利,则将权利移交给父要求, */
if (r == c->data) {
r->main->count--;
if (!r->logged) {
clcf = ngx_http_get_module_loc_conf(r, ngx_http_core_module);
if (clcf->log_subrequest) {
ngx_http_log_request(r);
}
r->logged = 1;
} else {
ngx_log_error(NGX_LOG_ALERT, c->log, 0,
"subrequest: "%V?%V" logged again",
&r->uri, &r->args);
}
r->done = 1;
/* 如果该子要求不是提早完成,则从父要求的postponed链表中删除 */
if (pr->postponed && pr->postponed->request == r) {
pr->postponed = pr->postponed->next;
}
/* 将发送权利移交给父要求,父要求下次履行的时候会发送它的postponed链表中可以
* 发送的数据节点,或将发送权利移交给它的下1个子要求 */
c->data = pr;
} else {
/* 该子要求提早履行完成,而且它没有产生任何数据,则它下次再次取得
* 履行机会时,将会履行ngx_http_request_finalzier函数,它实际上是履行
* ngx_http_finalzie_request(r,0),不做具体操作,直到它发送数据时,
* ngx_http_finalzie_request函数会将它从父要求的postponed链表中删除
*/
r->write_event_handler = ngx_http_request_finalizer;
if (r->waited) {
r->done = 1;
}
}
/* 将父要求加入posted_request队尾,取得1次运行机会 */
if (ngx_http_post_request(pr, NULL) != NGX_OK) {
r->main->count++;
ngx_http_terminate_request(r, 0);
return;
}
return;
}
/* 这里是处理主要求结束的逻辑,如果主要求有未发送的数据或未处理的子要求,
* 则给主要求添加写事件,并设置适合的write event hander,
* 以便下次写事件来的时候继续处理 */
if (r->buffered || c->buffered || r->postponed || r->blocked) {
if (ngx_http_set_write_handler(r) != NGX_OK) {
ngx_http_terminate_request(r, 0);
}
return;
}
...
}
父要求被激活后的回调方法
父要求被激活后的回调方法由指针 ngx_http_event_pt 实现。该方法负责把响应包发送给用户。以下所示:
typedef void(*ngx_http_event_handler_pt)(ngx_http_request_t *r);
struct ngx_http_request_s{
...
ngx_http_event_handler_pt write_event_handler;
...
};
1个要求中,只能调用1次 subrequest,即不能1次创建多个子要求,但是可以在新创建的子要求中再创建新的子要求。
参考资料:
《深入理解Nginx 》
《Emiller's Advanced Topics In Nginx Module Development》
《nginx subrequest的实现解析》
《ngx_http_request_t结构体》
