【边做项目边学Android】知识点:Intent
1. Intent的介绍
- Android中提供了Intent机制来协助利用间的交互与通讯,或采取更准确的说法是,Intent不但可用于利用程序之间,也可用于利用程序内部的activity, service和broadcast receiver之间的交互。
- Intent是1种运行时绑定(runtime binding)机制,它能在程序运行的进程中连接两个不同的组件。通过Intent,你的程序可以向Android表达某种要求或意愿,Android会根据意愿的内容选择适当的组件来响应。
Intent的中文意思是“意图,意向”,在Android中提供了Intent机制来协助利用间的交互与通讯,Intent负责对利用中1次操作的动作、动作触及数据、附加数据进行描写,Android则根据此Intent的描写,负责找到对应的组件,将 Intent传递给调用的组件,并完成组件的调用。Intent不但可用于利用程序之间,也可用于利用程序内部的Activity/Service之间的交互。因此,可以将Intent理解为不同组件之间通讯的“媒介”专门提供组件相互调用的相干信息,起着1个媒体中介的作用,专门提供组件相互调用的相干信息,实现调用者与被调用者之间的解耦。
Intent 是1个将要履行的动作的抽象的描写,1般来讲是作为参数来使用,由Intent来协助完成android各个组件之间的通讯。比如说调用 startActivity()来启动1个activity,或由broadcaseIntent()来传递给所有感兴趣的 BroadcaseReceiver, 再或由startService()/bindservice()来启动1个后台的service。所以可以看出来,intent主要是用来启动其他的 activity 或service,所以可以将intent理解成activity之间的粘合剂。
主要用处
Intent是1种消息传递机制,它可以在利用程序内使用,也能够在利用程序间使用,主要用处分为:
1.使用类名显示的启动1个特定的Activity或Service
2.启动Activity或Service来履行1个动作的Intent,通常需要使用特定的数据,或对特定的数据履行动作
3.广播某个事件已产生
activity、service和broadcast receiver之间是通过Intent进行通讯的,而另外1个组件Content Provider本身就是1种通讯机制,不需要通过Intent。我们来看下面这个图就知道了:
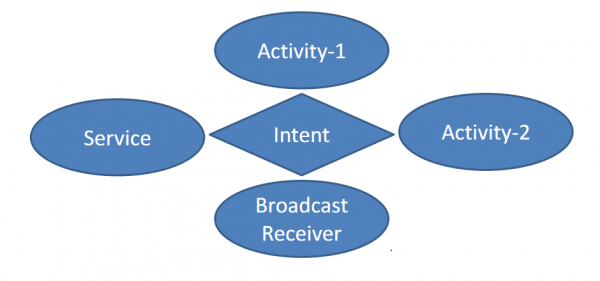
如果Activity1需要和Activity2进行联系,2者不需要直接联系,而是通过Intent作为桥梁。通俗来说,Intnet类似于中介、牙婆的角色。
Intent最多见的1个用法是显示的(通过指定要装载的类)或隐式的(通过要求对1条数据履行某个动作)启动新的activity,在后1种情况下,动作不1定由调用利用程序中的Activty履行。
Intent也能够在系统范围内发送广播消息。利用程序可以注册1个Broadcast Receiver来监听相应这些广播的Intent。Android就是通过广播Intent来公布系统事件,比如网络连接状态或电池电量的改变。
2. Inten启动组件的方法
Intent可以启动1个Activity,也能够启动1个Service,还可以发起1个广播Broadcasts。具体方法以下:
对向这3种组件发送intent有不同的机制:
- 使用Context.startActivity() 或 Activity.startActivityForResult(),传入1个intent来启动1个activity。使用 Activity.setResult(),传入1个intent来从activity中返回结果。
- 将intent对象传给Context.startService()来启动1个service或传消息给1个运行的service。将intent对象传给 Context.bindService()来绑定1个service。
- 将intent对象传给 Context.sendBroadcast(),Context.sendOrderedBroadcast(),或Context.sendStickyBroadcast()等广播方法,则它们被传给 broadcast receiver。
|
组件名称 |
方法名称 |
| Activity |
startActvity( ) startActivityForResult( ) |
| Service |
startService( ) bindService( ) |
| Broadcasts |
sendBroadcasts( ) sendOrderedBroadcasts( ) sendStickyBroadcasts( ) |
3. Intent的构成
Intent由以下各个组成部份:
- component(组件):目的组件
- action(动作):用来表现意图的行动
- category(种别):用来表现动作的种别
- data(数据):表示与动作要操纵的数据
- type(数据类型):对data范例的描述
- extras(扩大信息):扩大信息
- Flags(标志位):期望这个意图的运行模式
1、component(组件):目的组件
指定Intent的的目标组件的类名称。通常 Android会根据Intent 中包括的其它属性的信息,比如action、data/type、category进行查找,终究找到1个与之匹配的目标组件。但是,如果 component这个属性有指定的话,将直接使用它指定的组件,而不再履行上述查找进程。指定了这个属性以后,Intent的其它所有属性都是可选的。
例如,启动第2个Activity时,我们可以这样来写:
如果写的简单1点,监听事件onClick()方法里可以这样写:
Intent intent = new Intent(); //setClass函数的第1个参数是1个Context对象 //Context是1个类,Activity是Context类的子类,也就是说,所有的Activity对象,都可以向上转型为Context对象 //setClass函数的第2个参数是1个Class对象,在当前场景下,应当传入需要被启动的Activity类的class对象 intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class); startActivity(intent);
再简单1点,可以这样写:(固然,也是最多见的写法)
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,SecondActivity.class); startActivity(intent);
2、Action(动作):用来表现意图的行动
当平常生活中,描写1个意愿或欲望的时候,总是有1个动词在其中。比如:我想“做”3个俯卧撑;我要“写”1封情书,等等。在Intent中,Action就是描写做、写等动作的,当你指明了1个Action,履行者就会依照这个动作的唆使,接受相干输入,表现对应行动,产生符合的输出。在Intent类中,定义了1批量的动作,比如ACTION_VIEW,ACTION_PICK等, 基本涵盖了经常使用动作。加的动作越多,越精确。
标准的Activity Actions
ACTION_MAIN 作为1个主要的进入口,而其实不期望去接受数据
ACTION_VIEW 向用户去显示数据
ACTION_ATTACH_DATA 用于指定1些数据应当附属于1些其他的地方,例如,图片数据应当附属于联系人
ACTION_EDIT 访问已给的数据,提供明确的可编辑
ACTION_PICK 从数据当选择1个子项目,并返回你所选中的项目
ACTION_CHOOSER 显示1个activity选择器,允许用户在进程之前选择他们想要的
ACTION_GET_CONTENT 允许用户选择特殊种类的数据,并返回(特殊种类的数据:照1张相片或录1段音)
ACTION_DIAL 拨打1个指定的号码,显示1个带有号码的用户界面,允许用户去启动呼唤
ACTION_CALL 根据指定的数据履行1次呼唤
(ACTION_CALL在利用中启动1次呼唤有缺点,多数利用ACTION_DIAL,ACTION_CALL不能用在紧急呼唤上,紧急呼唤可以用ACTION_DIAL来实现)
ACTION_SEND 传递数据,被传送的数据没有指定,接收的action要求用户发数据
ACTION_SENDTO 发送1个信息到指定的某人
ACTION_ANSWER 处理1个打进电话呼唤
ACTION_INSERT 插入1条空项目到已给的容器
ACTION_DELETE 从容器中删除已给的数据
ACTION_RUN 运行数据,不管怎样
ACTION_SYNC 同步履行1个数据
ACTION_PICK_ACTIVITY 为已知的Intent选择1个Activity,返回别选中的类
ACTION_SEARCH 履行1次搜索
ACTION_WEB_SEARCH 履行1次web搜索
ACTION_FACTORY_TEST 工场测试的主要进入点,
标准的广播Actions
ACTION_TIME_TICK 当前时间改变,每分钟都发送,不能通过组件声明来接收,只有通过Context.registerReceiver()方法来注册
ACTION_TIME_CHANGED 时间被设置
ACTION_TIMEZONE_CHANGED 时间区改变
ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED 系统完成启动后,1次广播
ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED 1个新利用包已安装在装备上,数据包括包名(最新安装的包程序不能接收到这个广播)
ACTION_PACKAGE_CHANGED 1个已存在的利用程序包已改变,包括包名
ACTION_PACKAGE_REMOVED 1个已存在的利用程序包已从装备上移除,包括包名(正在被安装的包程序不能接收到这个广播)
ACTION_PACKAGE_RESTARTED 用户重新开始1个包,包的所有进程将被杀死,所有与其联系的运行时间状态应当被移除,包括包名(重新开始包程序不能接收到这个广播)
ACTION_PACKAGE_DATA_CLEARED 用户已清楚1个包的数据,包括包名(清除包程序不能接收到这个广播)
ACTION_BATTERY_CHANGED 电池的充电状态、电荷级别改变,不能通过组建声明接收这个广播,只有通过Context.registerReceiver()注册
ACTION_UID_REMOVED 1个用户ID已从系统中移除
3、category(种别):用来表现动作的种别
Intent中的Category属性是1个履行动作Action的附加信息。比如:CATEGORY_HOME则表示放回到Home界面,ALTERNATIVE_CATEGORY表示当前的Intent是1系列的可选动作中的1个。
指定Action范围,这个选项指定了将要履行的这个action的其他1些额外的束缚。有时通过Action,配合Data 或Type,很多时候可以准确的表达出1个完全的意图了,但也会需要加1些束缚在里面才能够更精准。比如,如果你虽然很喜欢做俯卧撑,但1次做3个还只是在特殊的时候才会产生,那末你可能表达说:每次吃撑了的时候 ,我都想做3个俯卧撑。吃撑了,这就对应着Intent的Category的范畴,它给所产生的意图附加1个束缚。在Android中,1个实例是:所有利用的主Activity(单独启动时候,第1个运行的那个Activity...),都需要1个Category为 CATEGORY_LAUNCHER,Action为ACTION_MAIN的Intent。
在自定义动作时,使用activity组件时,必须添加1个默许的种别
具体的实现为:
每一个Intent中只能指定1个action,但却能指定多个category;种别越多,动作越具体,意图越明确(类似于相亲时,给对方提了很多要求)。
自定义种别: 在Intent添加种别可以添加多个种别,那就要求被匹配的组件必须同时满足这多个种别,才能匹配成功。操作Activity的时候,如果没有种别,须加上默许种别
| Constant | Meaning |
CATEGORY_BROWSABLE |
The target activity can be safely invoked by the browser to display data referenced by a link ― for example, an image or an e-mail message. |
CATEGORY_GADGET |
The activity can be embedded inside of another activity that hosts gadgets. |
CATEGORY_HOME |
The activity displays the home screen, the first screen the user sees when the device is turned on or when the HOME key is pressed. |
CATEGORY_LAUNCHER |
The activity can be the initial activity of a task and is listed in the top-level application launcher. |
CATEGORY_PREFERENCE |
The target activity is a preference panel. |
4、data(数据):表示与动作要操纵的数据
- Data属性是Android要访问的数据,和action和Category声明方式相同,也是在<intent-filter>中。
- 多个组件匹配成功显示优先级高的; 相同显示列表。
Data是用1个uri对象来表示的,uri代表数据的地址,属于1种标识符。通常情况下,我们使用action+data属性的组合来描写1个意图:做甚么
使用隐式Intent,我们不但可以启动自己程序内的活动,还可以启动其他程序的活动,这使得Android多个利用程序之间的功能同享成了可能。比如利用程序中需要展现1个网页,没有必要自己去实现1个阅读器(事实上也不太可能),而是只需要条用系统的阅读器来打开这个网页就好了。
- 当Intent匹配成功的组件有多个时,显示优先级高的组件,如果优先级相同,显示列表让用户自己选择
- 优先级从⑴000至1000,并且其中1个必须为负的才有效
注:系统默许的阅读器并没有做出优先级声明,其优先级默许为正数。
Data属性的声明中要指定访问数据的Uri和MIME类型。可以在<data>元素中通过1些属性来设置:
android:scheme、android:path、 android:port、android:mimeType、android:host等,通过这些属性来对应1个典型的Uri格式 scheme://host:port/path。例如:http://www.google.com。
5、type(数据类型):对data范例的描述
如果Intent对象中既包括Uri又包括Type,那末,在<intent-filter>中也必须2者都包括才能通过测试。
Type属性用于明确指定Data属性的数据类型或MIME类型,但是通常来讲,当Intent不指定Data属性时,Type属性才会起作用,否则Android系统将会根据Data属性值来分析数据的类型,所以无需指定Type属性。
data和type属性1般只需要1个,通过setData方法会把type属性设置为null,相反设置setType方法会把data设置为null,如果想要两个属性同时设置,要使用Intent.setDataAndType()方法。
6、extras(扩大信息):扩大信息
是其它所有附加信息的集合。使用extras可以为组件提供扩大信息,比如,如果要履行“发送电子邮件”这个动作,可以将电子邮件的标题、正文等保存在extras里,传给电子邮件发送组件。
7、Flags(标志位):期望这个意图的运行模式
1个程序启动后系统会为这个程序分配1个task供其使用,另外同1个task里面可以具有不同利用程序的activity。那末,同1个程序能不能具有多个task?这就触及到加载activity的启动模式,这个需要单独讲1下。能辨认,有输入,全部Intent基本就完全了,但还有1些附件的指令,需要放在Flags中带过去。顾名思义,Flags是1个整形数,有1些列的标志 位构成,这些标志,是用来指明运行模式的。比如,你期望这个意图的履行者,和你运行在两个完全不同的任务中(或说进程也无妨吧...),就需要设置FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK 的标志位。
注:android中1组逻辑上在1起的activity被叫做task,自己认为可以理解成1个activity堆栈。
Intent 的解析机制
理解Intent的关键之1是理解清楚Intent的两种基本用法:1种是显式的Intent,即在构造Intent对象时就指定接收者;另外一种是隐式的Intent,即Intent的发送者在构造Intent对象时,其实不知道也不关心接收者是谁,有益于下降发送者和接收者之间的耦合。官方建议使用隐式Intent。上述属性中,component属性为直接类型,其他均为间接类型。
对显式Intent,Android不需要去做解析,由于目标组件已很明确,Android需要解析的是那些隐式Intent,通过解析,将 Intent映照给可以处理此Intent的Activity、IntentReceiver或Service。
相比与显式Intent,隐式Intnet则涵蓄了许多,它其实不明确指出我们想要启动哪个活动,而是指定1系列更加抽象的action和category等信息,然后交由系统去分析这个Intent,并帮我们找出适合的活动去启动。
Activity 中 Intent Filter 的匹配进程 :
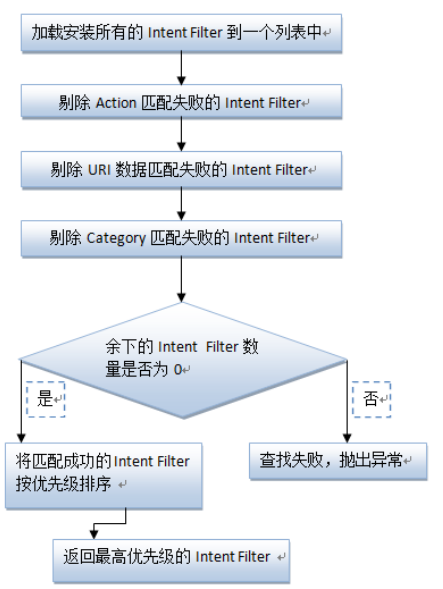
Intent 解析机制主要是通过查找已注册在AndroidManifest.xml中的所有IntentFilter及其中定义的Intent,终究找到匹配的 Intent。在这个解析进程中,Android是通过Intent的action、type、category这3个属性来进行判断的,判断方法以下:
- 如果Intent指明定了action,则目标组件的IntentFilter的action列表中就必须包括有这个action,否则不能匹配;
- 如果Intent没有提供type,系统将从data中得到数据类型。和action1样,目标组件的数据类型列表中必须包括Intent的数据类型,否则不能匹配。
- 如果Intent中的数据不是content: 类型的URI,而且Intent也没有明确指定它的type,将根据Intent中数据的scheme (比如 http: 或mailto:) 进行匹配。同上,Intent 的scheme必须出现在目标组件的scheme列表中。
- 如果Intent指定了1个或多个category,这些种别必须全部出现在组建的种别列表中。比如Intent中包括了两个种别:LAUNCHER_CATEGORY 和 ALTERNATIVE_CATEGORY,解析得到的目标组件必须最少包括这两个种别。
Intent-Filter的定义
1些属性设置的例子:
完全的实例
<activity android:name="NotesList" android:label="@string/title_notes_list"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" /> <action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" /> <action android:name="android.intent.action.PICK" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <data android:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.dir/vnd.google.note" /> </intent-filter> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.GET_CONTENT" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" /> <data android:mimeType="vnd.android.cursor.item/vnd.google.note" /> </intent-filter> </activity>
Intent的构造函数
公共构造函数:
1、Intent() 空构造函数
2、Intent(Intent o) 拷贝构造函数
3、Intent(String action) 指定action类型的构造函数
4、Intent(String action, Uri uri) 指定Action类型和Uri的构造函数,URI主要是结合程序之间的数据同享ContentProvider
5、Intent(Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) 传入组件的构造函数,也就是上文提到的
6、Intent(String action, Uri uri, Context packageContext, Class<?> cls) 前两种结合体
Intent有6种构造函数,3、4、5是最经常使用的,其实不是其他没用!
Intent(String action, Uri uri) 的action就是对应在AndroidMainfest.xml中的action节点的name属性值。在Intent类中定义了很多的Action和Category常量。
示例代码2:
示例代码2是用了第4种构造函数,只是uri参数为null。履行此代码的时候,系统就会在程序主配置文件AndroidMainfest.xml中寻觅
<action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" />对应的Activity,如果对应为多个activity具有<action android:name="android.intent.action.EDIT" />此时就会弹出1个dailog选择Activity。
如果是用示例代码1那种方式进行发送则不会有这类情况。
利用Intent在Activity之间传递数据
在Main中履行以下代码:
以上代码就实现了Activity之间的数据传递!
总结说明
这篇文章是我刚开始学习Android时看到的,当时理解的不是很深入,现在再回头看这篇文章总结的很详细,在这里与大家分享。
1,调用web阅读器
7,播放
8,调用发邮件
用获得到的Intent直接调用startActivity(returnIt)就ok了。
Intent用法实例
1、打开指定网页:(直接复制的上面的代码)
MainActivity.java中,监听器部份的核心代码以下:
第5行代码:通过Uri.parse()方法,将1个网址字符串解析成1个Uri对象,再调用intent的setData()方法将这个Uri对象传递进去。
2、打电话:
【方式1】打开拨打电话的界面:
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DIAL); intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:10086")); startActivity(intent);
运行程序后,点击按钮,显示以下界面:
【方式2】直接拨打电话:
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_CALL); intent.setData(Uri.parse("tel:10086")); startActivity(intent);
要使用这个功能必须在配置文件中加入权限:(加1行代码)
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" android:targetSdkVersion="16" /> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CALL_PHONE"/>
3、发送短信:
【方式1】打开发送短信的界面:action+type
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW); intent.setType("vnd.android-dir/mms-sms"); intent.putExtra("sms_body", "具体短信内容"); //"sms_body"为固定内容 startActivity(intent);
【方式2】打开发短信的界面(同时指定电话号码):action+data
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_SENDTO); intent.setData(Uri.parse("smsto:18780260012")); intent.putExtra("sms_body", "具体短信内容"); //"sms_body"为固定内容 startActivity(intent);
4、播放指定路径音乐:action+data+type
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW); Uri uri = Uri.parse("file:///storage/sdcard0/平凡之路.mp3"); ////路径也能够写成:"/storage/sdcard0/平凡之路.mp3" intent.setDataAndType(uri, "audio/mp3"); //方法:Intent android.content.Intent.setDataAndType(Uri data, String type) startActivity(intent);
5、卸载程序:action+data(例如点击按钮,卸载某个利用程序,根据包名来辨认)
注:不管是安装还是卸载,利用程序是根据包名package来辨认的。
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_DELETE); Uri data = Uri.parse("package:com.example.smyh006intent01"); intent.setData(data); startActivity(intent);
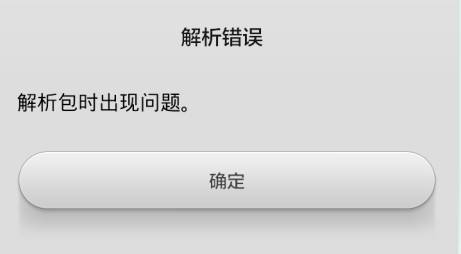
6、安装程序:action+data+type
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW); Uri data = Uri.fromFile(new File("/storage/sdcard0/AndroidTest/smyh006_Intent01.apk")); //路径不能写成:"file:///storage/sdcard0/···" intent.setDataAndType(data, "application/vnd.android.package-archive"); //Type的字符串为固定内容 startActivity(intent);
注:第2行的路径不能写成:"file:///storage/sdcard0/・・・",不然报错以下:
综上所述,完全版代码以下:
MainActivity.java代码以下:
1.无参数Activity跳转
Intent it = new Intent(Activity.Main.this, Activity2.class); startActivity(it);
2.向下1个Activity传递数据(使用Bundle和Intent.putExtras)
Intent it = new Intent(Activity.Main.this, Activity2.class); Bundle bundle=new Bundle(); bundle.putString("name", "This is from MainActivity!"); it.putExtras(bundle); // it.putExtra(“test”, "shuju”); startActivity(it); // startActivityForResult(it,REQUEST_CODE);
对数据的获得可以采取:
Bundle bundle=getIntent().getExtras(); String name=bundle.getString("name");
3.向上1个Activity返回结果(使用setResult,针对startActivityForResult(it,REQUEST_CODE)启动的Activity)
Intent intent=getIntent(); Bundle bundle2=new Bundle(); bundle2.putString("name", "This is from ShowMsg!"); intent.putExtras(bundle2); setResult(RESULT_OK, intent);
4.回调上1个Activity的结果处理函数(onActivityResult)
@Override protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data); if (requestCode==REQUEST_CODE){ if(resultCode==RESULT_CANCELED) setTitle("cancle"); else if (resultCode==RESULT_OK) { String temp=null; Bundle bundle=data.getExtras(); if(bundle!=null) temp=bundle.getString("name"); setTitle(temp); } } }
运行后,主界面以下:
