J2EE开发框架搭建(6) - 使用hibernate4完成基本Dao的封装
栏目:互联网时间:2014-09-29 08:00:01
现在orm框架有很多,比如说guzz,hibernate,mybaits....,在封装一个框架的时候我们可以选择一种,也可以选择多种实现,供以后使用选择,这里我只实现了hibernate,目录结构图如下:
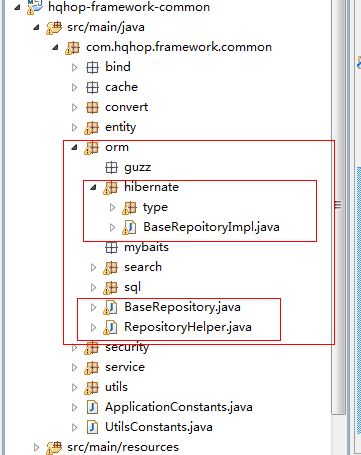
1. 首先查询BaseRepository这个接口,该接口泛型 :T 表示实体类型;ID表示主键类型;虽然在框架里面已经提供了查询的结构Searchable,但是Searchable也不能做到无限强大,比如一个多变关联查询,嵌套查询是没有办法完成的,所有只能自己编写sql语句,但是hibernate编写sql语句都只能写在java代码里面,用过mybaits的朋友就知道sql语句可以配置在xml里面 ,这里我们就可以简单的仿照mybaits来完成,在这个接口中就提供了调用xml中的sql语句的方法,具体怎么实现后面再说明:
package com.hqhop.framework.common.orm;
///import .....
/**
* <p>
* 抽象DAO层基类 提供一些简便方法<br/>
* <p/>
* <span style="color:#ff0000;">泛型 :T 表示实体类型;ID表示主键类型</span>
* <p>
* Version: 1.0
*
* @author silentwu
*/
public interface BaseRepository<T extends AbstractEntity<ID>, ID extends Serializable> extends PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> {
/**
* 根据主键删除
*
* @param ids
*/
public void delete(ID... ids);
/**
* 根据条件查询所有 条件 + 分页 + 排序
*
* @param searchable
* @return
*/
public Page<T> findAll(Searchable searchable);
/**
* 根据条件统计所有记录数
*
* @param searchable
* @return
*/
public long count(Searchable searchable);
public void update(T entity);
/**
* 自定义sql更新
*
* @param sqlKey
* @param params
*/
public void update(String sqlKey, Object... params);
/**
* 自定义sql查询
*
* @param sqlKey
* @param params
* @return
*/
public List<T> findAll(String sqlKey, Object... params);
public Page<T> findPage(Pageable pageable, String sqlKey, Object... params);
/**
* 自定义sql删除
*
* @param sqlKey
* @param params
*/
public void delete(String sqlKey, Object... params);
}
该接口继承了spring的PagingAndSortingRepository接口, 然而PagingAndSortingRepository又继承了CrudRepository接口,所以BaseRepository就具有了基本的增删改查以及自己定义的一些方法:
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> {
Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort);
Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable);
}
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends Repository<T, ID> {
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
<S extends T> Iterable<S> save(Iterable<S> entities);
T findOne(ID id);
boolean exists(ID id);
Iterable<T> findAll();
Iterable<T> findAll(Iterable<ID> ids);
long count();
void delete(ID id);
void delete(T entity);
void delete(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
void deleteAll();
}
2. 接下来查看BaseRepository的实现类BaseRepositoryImpl,由于要使用hibernate操作数据库,所以要提供session,在hibernate4中已经建议直接使用session操作数据库,建议不要在使用hibernateTemplate;要使用sessionFactory.getCurrentSession()来获取当前的线程中的session就必须开启事物,所以在spring-config.xml中加入下代码:
<!-- 开启注解事务 只对当前配置文件有效 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" proxy-target-class="true" />
<!-- 配置Hibernate事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.orm.hibernate4.HibernateTransactionManager">
<property name="sessionFactory" ref="sessionFactory" />
</bean>
在BaseRepositoryImpl就可以使用如下代码了:
@Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
public Session getSession() {
// 事务必须是开启的(Required),否则获取不到
return sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
}
3. 在BaseRepositoryImpl中还必须要有一个Class 属性,指定运行时刻BaseRepositoryImpl操作的实体类,因为在hibernate中做了sql查询或者是hql查询,查询的结果通过反射转化为实体类返回到service。那么又怎么给这个Class对象赋值呢?在这里我们需要自己定义一个注解Repository,在这个注解中就记录了BaseRepositoryImpl要操作的实体类:
/**
*
* @author silentwu
*
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@org.springframework.stereotype.Repository
public @interface Repository {
/**
* Repository在spring容器中的实例名称
*/
String value() default "";
/**
* Repository处理的实体类
*
* @return
*/
Class<?> entity();
}
接下来我们就可以直接在BaseRepositoryImpl中获取这个注解来得到Class,在BaseRepositoryImpl中添加如下代码:
private Class<T> clazz;
@PostConstruct
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void init() throws Exception {
<span style="color:#ff0000;">Repository repository = this.getClass().getAnnotation(Repository.class);</span>
if (Utils.isNotEmpty(repository)) {
if (Utils.isNotEmpty(repository.entity())) {
<span style="color:#ff0000;">this.clazz = (Class<T>) repository.entity();</span>
this.countAllQL = String.format(COUNT_QUERY_STRING, clazz.getName());
this.findAllQL = String.format(FIND_QUERY_STRING, clazz.getName());
} else {
throw new Exception(Repository.class + "注解的entity不能为空!");
}
} else {
throw new Exception(this.getClass() + " 必须要使用" + Repository.class + "注解!");
}
}
在init()方法上面添加了@PostConstruct注解,表示在类被spring容器实例化后要执行的方法;也可以实现spring的InitializingBean接口来达到同样的效果(但是spring已经不推荐使用这种方式)
4. 在前面的章节中,我们提供了逻辑删除的接口LogicDeleteable,具体实现逻辑的删除就是在BaseRepositoryImpl中,在BaseRepositoryImpl中提供了多个删除方法,但是主要的删除操作只有一个delete(T entity),其他的删除都是调用的这个:
/**
* 检查是否实现了逻辑删除接口
*
* @return
*/
private boolean checkLogicDeleteable() {
Class[] inters = this.clazz.getInterfaces();
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < inters.length; i++) {
if ("LogicDeleteable".equals(inters[i].getSimpleName())) {
flag = true;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
@Override
public void delete(T entity) {
if (Utils.isNotEmpty(entity)) {
if (entity instanceof LogicDeleteable) {
((LogicDeleteable) entity).markDeleted();
update(entity);
} else {
this.getSession().delete(entity);
}
}
}
在删除对象的时候首先判断是否实现了LogicDeleteable接口,若为true ==> 调用markDeleted(); 否则真实删除。5. BaseRepository,BaseRepositoryImpl的使用方式,操作User实体类:
接口UserDao
public interface UserDao extends BaseRepository<User, String> {
}
实现类UserDaoImpl,使用@Repository注解,指定操作的实体类
@Repository(entity = User.class)
public class UserDaoImpl extends BaseRepoitoryImpl<User, String> implements UserDao {
}
------分隔线----------------------------
------分隔线----------------------------